Learn how to set GRUB password in Linux to enhance your system’s security. Follow our step-by-step guide to protect your boot loader and prevent unauthorized access to boot settings. #centlinux #linux #grub
Table of Contents
What is GRUB?
GRUB (Grand Unified Bootloader) is a bootloader package developed to support multiple operating systems and allow the user to select among them during boot-up. It is commonly used in Unix-like operating systems, particularly Linux. Here are some key points about GRUB:
Functionality: GRUB loads the operating system kernel into memory and starts its execution. It is the first software program that runs when a computer starts.
Configuration: GRUB’s configuration file is usually located at /boot/grub/grub.cfg (for GRUB 2). This file is often generated by scripts and should not be edited directly. Instead, users typically edit /etc/default/grub and then run update-grub to apply changes.
Versions: There are two main versions of GRUB:
- GRUB Legacy: The original version, which is now largely deprecated.
- GRUB 2: The current version, which includes many improvements and new features.

Main Features
- Multi-boot support: Allows booting multiple operating systems.
- Scripting: Supports scripting for advanced configurations.
- File system support: Can read various file systems, enabling it to load kernels from different partitions.
- Theming: Supports graphical themes for a more user-friendly interface.
Boot Process
The GRUB (Grand Unified Bootloader) boot process is a critical sequence that loads the Linux kernel and initializes the operating system. Below is a detailed breakdown of the GRUB boot process:
1. Power-On and BIOS/UEFI Initialization
- When the system powers on, the BIOS (Legacy) or UEFI firmware initializes hardware.
- The firmware performs a Power-On Self-Test (POST) and detects bootable devices.
- The boot order (defined in BIOS/UEFI settings) determines which device (HDD, SSD, USB, etc.) is used to load the bootloader.
2. Loading GRUB (Stage 1)
In Legacy BIOS (MBR) Mode:
- The BIOS reads the Master Boot Record (MBR) (first 512 bytes of the boot disk).
- The MBR contains Stage 1 of GRUB, which is a small bootloader that loads the next stage.
- Since Stage 1 is limited in size, it only knows how to load Stage 1.5 (located in the boot partition’s unused sectors).
In UEFI Mode:
- UEFI looks for a FAT32 EFI System Partition (ESP) containing GRUB’s EFI executable (
grubx64.efi). - GRUB is loaded directly from the ESP without needing stages like MBR.
3. GRUB Stage 1.5 (Legacy BIOS Only)
- Stage 1.5 contains filesystem drivers (e.g.,
ext2,ext4,xfs) to read/boot. - It locates and loads Stage 2 (the main GRUB image) from
/boot/grub.
4. GRUB Stage 2 (Main Bootloader)
- Stage 2 loads the full GRUB interface, including:
- The GRUB configuration file (
/boot/grub/grub.cfgor/boot/grub2/grub.cfg). - Kernel and initramfs images (located in
/boot).
- The GRUB configuration file (
- GRUB displays a boot menu (if configured) allowing users to select an OS or kernel version.
5. Loading the Linux Kernel
- GRUB loads the selected Linux kernel (
vmlinuz-*) and initramfs (initial RAM filesystem) into memory. - The initramfs contains essential drivers and tools needed to mount the real root filesystem (especially important for encrypted disks or LVM).
6. Handing Over Control to the Kernel
- GRUB executes the kernel with specified boot parameters (
root=,ro,quiet, etc.). - The kernel takes over, initializes hardware, and mounts the root (
/) filesystem. - The initramfs runs
initscripts to prepare the system (e.g., unlocking encrypted disks). - Finally, the kernel starts the systemd (or SysV init) process (PID 1), which initializes user space.
Recovery and Customization
- Recovery: GRUB includes a command-line interface that can be used for troubleshooting and recovery if the system fails to boot.
- Customization: Users can customize the boot menu, set default boot options, and configure timeout settings.
GRUB Configuration Files
| File | Purpose |
|---|---|
/boot/grub/grub.cfg | Main GRUB configuration (auto-generated, do not edit manually). |
/etc/default/grub | Custom boot options (run update-grub after changes). |
/etc/grub.d/ | Scripts to generate grub.cfg (e.g., 40_custom for custom entries). |
GRUB is a powerful and flexible tool that plays a crucial role in the boot process of many systems, providing essential functionality for managing and booting multiple operating systems.
Why set GRUB Password?
You may be aware that, if a person has physical access to your Linux server. It can easily reset the superuser (root) password by booting your Linux OS into Single user mode.
For this purpose, one can easily edit the Kernel command in GRUB menu.
Therefore, it is a best practice to put a strong password on GRUB. So, whenever a user try to edit the menu entries, he has to provide a valid login/password.
Let’s see how we can set GRUB password on Linux Server. There are two ways to this.
The Simple Method
In some Linux distros such as Rocky Linux, RHEL or CentOS 8. GRUB bootloader is shipped with a handy command to set a password for boot menu.
This command sets a password for the default root user. Execute it now and set a strong password.
grub2-setpasswordReboot your Linux server to verify the new settings.
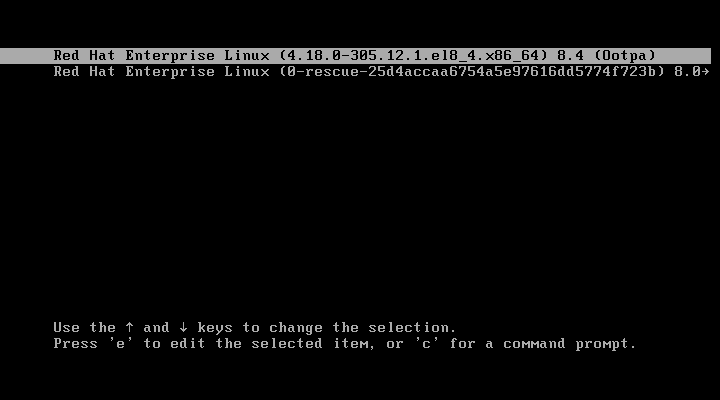
Press ‘e’ to edit the menu entries.

The GRUB is now asking for a login credentials. Enter the correct login/password.
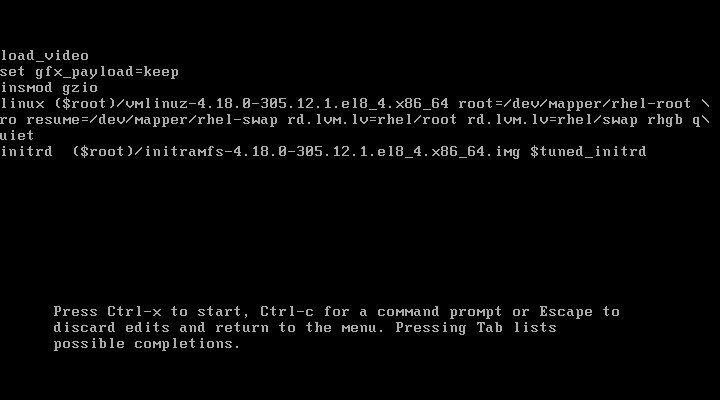
After providing valid credentials, you can now edit your GRUB menu commands.
Similarly, if you want to remove GRUB password, that was set by using the grub2-password command. You have to simply delete the following file.
rm -f /boot/grub2/user.cfg
rm -f /boot/efi/EFI/redhat/user.cfgFor a BIOS based system the user.cfg file is located in /boot/grub2/ directory, whereas on an UEFI based system, you may find it within /boot/efi/EFI/redhat/ directory.
Therefore, it is safe to delete it from both locations.
The Advance Method
If you want to create multiple login credentials for GRUB menu then the simple method won’t work for you.
Therefore, you have to use the following method to set passwords on boot menu. and this method works on all Linux distros that are using GRUB bootloader.
Execute the following command to generate password hashes for your users.
grub2-mkpasswd-pbkdf2
grub2-mkpasswd-pbkdf2Output:
Enter password:
Reenter password:
PBKDF2 hash of your password is grub.pbkdf2.sha512.10000.6CE9F4DAF8A6BB2823882EEF3A6CF1792523E4785BD891BF61597DE59BAEBF50787642196FDDC018258C7C00FBC105FAD3F7437936DCD0C72F925A101BADE2CE.EBD8D141809B5793651F198C91560FAB2A522683FB9E4BC95BE961D19A6A3E8F46225B7CF68A7F79BAAB19E99500FA6DC7CC6DB331026733670722D9FD40FDD4
Enter password:
Reenter password:
PBKDF2 hash of your password is grub.pbkdf2.sha512.10000.751F468CC621AF04393BD80D4C1B4C8D5D5B990A9CF6E2AEB7B1424ECE4ED2C4C9FD47FFE33156C11EADA59EFC7B16DBBED3F3A368468DC0A1FDEAEDEC2AB43D.37D24383BB42E891068090A0EF6E60B43F1C800F9A82F88179F7535343EEBAD08326BD1CBD3337ED5E712291B3DBDBB2341DF58E8F012F3D7E7CD10DE4F0B1A4
Edit /etc/grub.d/00_header by using your favorite text editor.
vi /etc/grub.d/00_headerAdd following lines of code at the end of this file.
cat << EOF
set superusers="grubadmin,gruboper"
password_pbkdf2 grubadmin grub.pbkdf2.sha512.10000.6CE9F4DAF8A6BB2823882EEF3A6CF1792523E4785BD891BF61597DE59BAEBF50787642196FDDC018258C7C00FBC105FAD3F7437936DCD0C72F925A101BADE2CE.EBD8D141809B5793651F198C91560FAB2A522683FB9E4BC95BE961D19A6A3E8F46225B7CF68A7F79BAAB19E99500FA6DC7CC6DB331026733670722D9FD40FDD4
password_pbkdf2 gruboper grub.pbkdf2.sha512.10000.751F468CC621AF04393BD80D4C1B4C8D5D5B990A9CF6E2AEB7B1424ECE4ED2C4C9FD47FFE33156C11EADA59EFC7B16DBBED3F3A368468DC0A1FDEAEDEC2AB43D.37D24383BB42E891068090A0EF6E60B43F1C800F9A82F88179F7535343EEBAD08326BD1CBD3337ED5E712291B3DBDBB2341DF58E8F012F3D7E7CD10DE4F0B1A4
EOFRebuild GRUB configuration file by executing following command.
grub2-mkconfig > /boot/grub2/grub.cfgOutput:
Generating grub configuration file ...
done
Above command may not be available on some Linux distros such as Debian, where you can alternatively execute following command.
update-grubSimilarly, if you want to remove the password from boot menu, you can remove this code from /etc/grub.d/00_header and regenerate the GRUB configurations.
A Bonus Tip: GRUB Boot Loader
Here, GRUB bootloader will ask for a login credential when user try to edit the menu. However, in some situations you may be required to set a password whenever you try to start your Linux OS.
Edit /etc/grub.d/10_linux in vim text editor.
vi /etc/grub.d/10_linuxFind following line in this file.
CLASS="--class gnu-linux --class gnu --class os --unrestricted"And remove the –unrestricted option.
CLASS="--class gnu-linux --class gnu --class os"Regenerate GRUB configuration file and reboot.

Now, GRUB will ask you for a password if you try to boot your Linux OS.
Beware that, if you forget this password, then you have to recover GRUB bootloader.
Video Tutorial: How to set GRUB Password in Linux
If you prefer a step-by-step visual guide, check out our detailed video tutorial on How to Set a GRUB Password in Linux. The video walks you through the entire process, from accessing the GRUB configuration file to setting up a secure password for protecting your bootloader. This tutorial is especially helpful for users who want a hands-on demonstration of the commands and configurations needed. Watch the video to ensure your Linux system is protected from unauthorized access right from the boot process.
Final Thoughts
Setting a GRUB password in Linux is a crucial security measure to prevent unauthorized access to bootloader settings. By securing GRUB, you can restrict users from modifying kernel parameters or booting into single-user mode without authentication.
After configuring the password, always test your setup to ensure it works as expected. Implementing this additional layer of security enhances system protection, especially on shared or sensitive environments. For a step-by-step visual guide, check out our video tutorial to see the process in action.
Looking for a Linux server expert? I provide top-tier administration, performance tuning, and security solutions for your Linux systems. Explore my Freelancer profile for details!
FAQs
Q1: Why should I set a GRUB password on my Linux system?
A1: It prevents unauthorized users from editing boot options or booting into single-user mode, adding an extra layer of security.
Q2: Can I change or remove the GRUB password later?
A2: Yes, by editing the GRUB configuration files and removing or updating the password entries, you can modify or remove the password.
Q3: Will setting a GRUB password affect automatic system updates?
A3: No, but you’ll need to re-enter the password if you manually edit boot options during updates or troubleshooting.
Q4: Is it necessary to encrypt the password file used in GRUB?
A4: The password is stored in plain text within configuration files, but it’s recommended to keep your system secure overall, as the password prevents unauthorized access at boot.
Q5: Can I set different GRUB passwords for different Linux distributions on the same machine?
A5: Yes, but you need to configure each distribution’s GRUB separately, as they manage their own bootloader configurations.
Recommended Courses
If you’re serious about building a career in IT, the Complete Linux Training Course to Get Your Dream IT Job 2025 by Imran Afzal is one of the best investments you can make in yourself. This highly rated course takes you from the basics of Linux to advanced system administration skills, preparing you for real-world IT roles and certifications.
Whether you’re a beginner or brushing up your skills, the structured lessons, hands-on labs, and career-oriented approach make it a perfect choice to boost your confidence and job readiness. Enroll now and start your Linux journey today!
Disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links. If you purchase through these links, I may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you. This helps support the site and allows me to continue creating valuable content.


Leave a Reply
Please log in to post a comment.