Discover how to install SquidAnalyzer on CentOS 7 with our detailed step-by-step guide. Enhance your web traffic analysis with this powerful tool and easy installation process. #centlinux #linux #squidproxy
Table of Contents
What is SquidAnalyzer?
SquidAnalyzer is an open-source tool designed to analyze and report on the logs generated by the Squid proxy server. It provides detailed statistics and visual reports on web traffic, making it easier for administrators to monitor and optimize their network usage. Here are some key features and aspects of SquidAnalyzer:
- Web Traffic Analysis: SquidAnalyzer processes Squid logs to generate comprehensive reports on web traffic. This includes information on visited URLs, bandwidth usage, and the most frequently accessed websites.
- User-Friendly Reports: The tool produces HTML reports that are easy to navigate, with graphs and charts that visually represent the data. This makes it simpler for administrators to understand usage patterns and identify potential issues.
- Detailed Statistics: It provides in-depth statistics on various aspects of web traffic, including user activity, domains accessed, and file types downloaded. This granularity helps in pinpointing specific usage trends and behaviors.
- Customizable: SquidAnalyzer can be customized to fit specific needs, such as setting up filters to exclude certain types of traffic or focusing on particular aspects of the data.
- Lightweight and Efficient: The tool is designed to be lightweight, ensuring it does not add significant overhead to the server. It efficiently processes large log files and generates reports quickly.
- Open Source: Being open source, SquidAnalyzer is freely available and can be modified to suit particular requirements. The community-driven development ensures it stays up-to-date with new features and improvements.
- Integration: SquidAnalyzer can be integrated with other tools and scripts to automate reporting and enhance its functionality within a broader network management system.
Overall, SquidAnalyzer is a valuable tool for network administrators who need to keep track of web traffic and optimize the performance and security of their network.
We install Squid proxy server on CentOS 7 in our previous article. Now, we are installing SquidAnalyzer for Squid log analysis on the same CentOS 7 server to have a analytical view of Squid logs.
Recommended Online Training: Learn Bash Shell in Linux for Beginners

Linux Server Specification
We have provisioned a CentOS 7 virtual machine with following specification.
- CPU – 3.4 Ghz (1 Core)
- Memory – 1 GB
- Storage – 20 GB
- Operating System – CentOS 7.7
- Hostname – squid-proxy-01.example.com
- IP Address – 192.168.116.214/24
Read Also: How to install CNTLM on Linux
Install SquidAnalyzer Prerequisites
SquidAnalyzer is a web based software therefore, we are required to install a web server to deploy and run SquidAnalyzer.
Install Apache HTTP Server using yum command.
# yum install -y httpd
SquidAnalyzer also requires perl compiler for installation.
Install perl packages using yum command.
# yum install -y perl perl-devel
We are also required git command to clone the SquidAnalyzer source from GitHub.
# yum install -y git
Install SquidAnalyzer on CentOS 7
Download the source code of SquidAnalyzer using git command.
# cd /var/www # git clone https://github.com/darold/squidanalyzer Cloning into 'squidanalyzer'... remote: Enumerating objects: 2064, done. remote: Total 2064 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 2064 Receiving objects: 100% (2064/2064), 1.44 MiB | 640.00 KiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (1309/1309), done.
Compile SquidAnalyzer from source code.
# cd squidanalyzer/ # perl Makefile.PL which: no bzcat in (/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin) Checking if your kit is complete... Looks good Writing Makefile for SquidAnalyzer Done... Now type 'make && make install'
You can now install SquidAnalyzer on CentOS 7 as follows.
# make && make install
cp SquidAnalyzer.pm blib/lib/SquidAnalyzer.pm
cp squid-analyzer blib/script/squid-analyzer
/usr/bin/perl -MExtUtils::MY -e 'MY->fixin(shift)' -- blib/script/squid-analyzer
Manifying blib/man3/SquidAnalyzer.3pm
Installing /usr/local/share/perl5/SquidAnalyzer.pm
sh install_all.sh
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Modify your httpd.conf to allow access to HTML output like follow:
Alias /squidreport /var/www/squidanalyzer
<Directory /var/www/squidanalyzer>
Options -Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews
AllowOverride None
Order deny,allow
Deny from all
Allow from 127.0.0.1
</Directory>
2. If necessary, give additional host access to SquidAnalyzer in httpd.conf.
Restart and ensure that httpd is running.
3. Browse to http://my.host.dom/squidreport/ to ensure that things are working
properly.
4. Setup a cronjob to run squid-analyzer daily:
# SquidAnalyzer log reporting daily
0 2 * * * /usr/local/bin/squid-analyzer > /dev/null 2>&1
or run it manually. For more information, see /README file.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Appending installation info to /usr/lib64/perl5/perllocal.podEdit Apache configuration to add SquidAnalyzer website.
# cd # vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/squidanalyzer.conf
Add following directives in configuration file.
Alias /squidreport /var/www/squidanalyzer
<Directory /var/www/squidanalyzer>
Options -Indexes +FollowSymLinks +MultiViews
AllowOverride None
Order deny,allow
Deny from all
Allow from 192.168.116.0/24
</Directory>Enable and start httpd.service.
# systemctl enable --now httpd Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.
Configure Linux Firewall
Allow HTTP service in CentOS 7 firewall.
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http success # firewall-cmd --reload success
Set Proxy Server Logfile Location
By default the log file location, provided in squidanalyzer.conf file is incorrect according to our Linux distro. Therefore, we need to correct it before moving forward.
# grep LogFile /etc/squidanalyzer/squidanalyzer.conf LogFile /var/log/squid3/access.log # sed -i 's/squid3/squid/' /etc/squidanalyzer/squidanalyzer.conf # grep LogFile /etc/squidanalyzer/squidanalyzer.conf LogFile /var/log/squid/access.log
Create a Cron Job for SquidAnalyzer
Configure a Cron job for SquidAnalyzer to generate analytical reports.
# crontab -e
add following lines therein.
# SquidAnalyzer log reporting daily 0 2 * * * /usr/local/bin/squid-analyzer > /dev/null 2>&1
We have to explicitly execute squid-analyzer command one time to generate reports in /var/www/squidanalyzer directory.
# /usr/local/bin/squid-analyzer
Access SquidAnalyzer Web UI
Open URL http://squid-proxy-01.example.com/squidreport in a web browser.
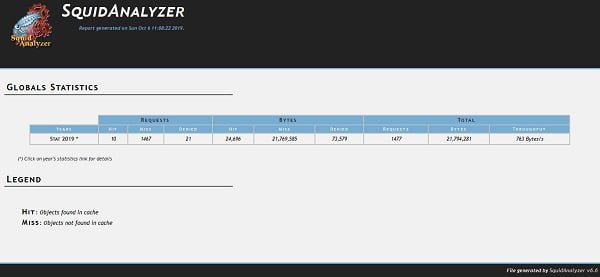


Configure HTTP Basic Authentication
SquidAnalyzer does not provides a native authentication method.
Since the SquidAnalyzer running as a web application, therefore, we can utilize the HTTP basic authentication to restrict the access to SquidAnalyzer website.
Install httpd-tools using yum command.
# yum install -y httpd-tools Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.ges.net.pk * extras: mirrors.ges.net.pk * updates: mirrors.ges.net.pk Package httpd-tools-2.4.6-90.el7.centos.x86_64 already installed and latest version Nothing to do
Nothing to do! because, we have already installed httpd-tools during installation of Squid proxy server on CentOS 7.
Create a password file for SquidAnalyzer and add squidadmin user therein.
# htpasswd -c /etc/squidanalyzer/passwd squidadmin New password: Re-type new password: Adding password for user squidadmin
Edit Apache configurations to add HTTP basic authentication.
# vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/squidanalyzer.conf
Add HTTP basic authentication for SquidAnalyzer. Final configuration should be look like this.
Alias /squidreport /var/www/squidanalyzer
<Directory /var/www/squidanalyzer>
Options -Indexes +FollowSymLinks +MultiViews
AllowOverride None
Order deny,allow
Deny from all
Allow from 192.168.116.0/24
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Restricted Content"
AuthUserFile /etc/squidanalyzer/passwd
Require valid-user
</Directory>Test Apache configuration files for syntax errors.
# httpd -t Syntax OK
Restart Apache service to take changes in effect.
# systemctl restart httpd.service
Open URL http://squid-proxy-01.example.com/squidreport in a web browser.
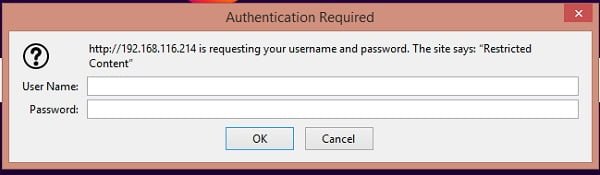
Now, it requires user authentication for access to SquidAnalyzer website.
If you are new to Linux and facing difficulty in working at Linux Bash prompt. We recommend that, you should read The Linux Command Line, 2nd Edition: A Complete Introduction by William Shotts.
Final Thoughts
Installing SquidAnalyzer on CentOS 7 is a great way to enhance your web traffic analysis capabilities. With detailed insights and easy installation, SquidAnalyzer helps you manage and optimize your network effectively.
If you need expert assistance with installing and configuring SquidAnalyzer on CentOS 7, I offer professional services to ensure a smooth and successful setup. Visit my Fiverr gig for more details and to get started: Linux Admin Expert
Optimize your network analysis with expert help. Contact me today!
