Want full control over your code? Learn how to install GitLab on CentOS 7 and unlock a powerful DevOps platform before you’re stuck relying on third-party services. Follow this step-by-step guide to set up your own Git repository manager today—don’t get left behind! #centlinux #linux #git
Table of Contents
What is GitLab?
GitLab is an open-source web-based git repository manager providing wiki, issue-tracking and CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Common Deployment). GitLab available in two editions, CE (Community Edition) and EE (Enterprise Edition). The GitLab CE has limited features while the GitLab EE is the commercial product and loaded with many additional features. Both GitLab CE & EE editions are available to download, however, the GitLab EE will provides same features as GitLab CE unless one acquires a license from GitLab. In this article, we will install GitLab on CentOS 7.
GitLab is a comprehensive DevOps platform designed for the entire software development lifecycle. It integrates tools for version control, project management, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD), and more. GitLab provides a single application for managing your development processes, enabling teams to collaborate effectively and streamline workflows.

Here’s a detailed overview of GitLab, including its features, components, and use cases:
Key Features of GitLab
- Version Control
- Git Repository Management: GitLab uses Git as its version control system, allowing users to manage code repositories with features like branching, merging, and pull requests.
- Code Review: Supports code reviews through merge requests where team members can comment, review, and approve changes.
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
- CI/CD Pipelines: Automate the process of building, testing, and deploying code changes. Pipelines can be configured using
.gitlab-ci.ymlfiles to define stages, jobs, and scripts. - Automated Testing: Run automated tests as part of the CI process to ensure code quality and detect issues early.
- Deployment: Deploy code to different environments (development, staging, production) as part of the CD process.
- CI/CD Pipelines: Automate the process of building, testing, and deploying code changes. Pipelines can be configured using
- Project Management
- Issue Tracking: Manage tasks, bugs, and feature requests using GitLab’s issue tracker. Issues can be assigned, labeled, and prioritized.
- Boards: Visualize and manage work with Kanban-style boards for tracking the progress of tasks and issues.
- Milestones: Organize issues and merge requests into milestones to track project goals and deadlines.
- Code Collaboration
- Merge Requests: Facilitate code reviews and collaborative development by requesting changes to be merged from one branch to another.
- Discussion Threads: Engage in discussions within issues and merge requests to review code and provide feedback.
- Security and Compliance
- Vulnerability Management: Scan code for security vulnerabilities and manage remediation.
- Compliance Management: Ensure compliance with various standards and regulations through features like audit logs and access controls.
- Secrets Management: Securely manage and access secrets and environment variables used in CI/CD pipelines.
- Repository Management
- Repository Hosting: Host Git repositories with features like repository mirroring, backups, and versioning.
- File Management: Manage files within repositories, including large files through Git LFS (Large File Storage).
- DevOps Lifecycle Integration
- DevOps Tools: Integrates with tools for monitoring, performance analysis, and incident management.
- API Access: Provides APIs for integration with external tools and automation of tasks.
- Documentation
- Wiki: Create and maintain project documentation using GitLab’s built-in Wiki feature.
- Documentation Pages: Generate and host project documentation with support for markdown and rich text.
Recommended Training: GitLab CI/CD Bootcamp| Zero to Hero| Certification Prep 2024 from Karan Gupta

Components of GitLab
- GitLab Community Edition (CE)
- Free and Open Source: Includes core features for version control, CI/CD, and basic project management.
- Features: Includes repository management, issue tracking, and CI/CD pipelines.
- GitLab Enterprise Edition (EE)
- Paid Version: Offers additional features and support for larger teams and organizations.
- Features: Includes advanced security, compliance tools, and enterprise-level support.
- GitLab.com
- Hosted Service: A cloud-hosted version of GitLab available as a SaaS (Software as a Service) offering.
- Plans: Free and paid plans with varying levels of features and support.
Common GitLab Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
gitlab-rails console | Open the Rails console for administrative tasks. |
gitlab-ctl reconfigure | Reconfigure GitLab after changes to configuration files. |
gitlab-ctl restart | Restart GitLab services. |
gitlab-ctl status | Check the status of GitLab services. |
gitlab-ctl upgrade | Upgrade GitLab to the latest version. |
GitLab vs. Other Git Platforms
| Feature | GitLab | GitHub | Bitbucket |
|---|---|---|---|
| Version Control | Git | Git | Git, Mercurial |
| CI/CD | Built-in CI/CD Pipelines | GitHub Actions (newer feature) | Built-in Pipelines (Bitbucket Pipelines) |
| Issue Tracking | Advanced issues and boards | Basic issues and projects | Basic issues and boards |
| Project Management | Advanced boards, milestones | Projects and basic task management | Advanced boards, milestones |
| Security | Advanced security features | Basic security features | Basic security features |
| Code Review | Merge Requests and code review | Pull Requests and code review | Pull Requests and code review |
| Free Tier | Generous free tier with CI/CD | Free tier with limited features | Free tier with limited features |
Use Cases
- Version Control: Manage and track changes in your source code.
- Collaborative Development: Work on projects with multiple team members.
- Continuous Integration: Automate testing and building of code.
- Continuous Deployment: Automate the deployment of applications.
- Project Management: Track tasks, milestones, and progress.
- Security Management: Scan for vulnerabilities and manage compliance.
Summary
GitLab is a powerful, integrated DevOps platform offering a suite of tools for version control, project management, CI/CD, and more. Whether you’re managing a personal project or working as part of a large team, GitLab provides the features you need to streamline development processes and ensure successful project outcomes.
Linux Server Specification
We have configured a Linux virtual machine with following specification for installing GitLab Server .
- Hostname – gitlab-server.itlab.com
- IP Address – 192.168.116.128/24
- CPU – 3.2 Ghz (2 Cores)
- Memory – 3 GB
- Storage – 60 GB
Read Also: How to install GitLab on CentOS 8
Amazon Fire HD 10 tablet (newest model) built for relaxation, 10.1″ vibrant Full HD screen, octa-core processor, 3 GB RAM, 32 GB, Ocean
$69.99 (as of July 9, 2025 21:12 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Install GitLab on CentOS 7
Connect to Linux Server (gitlab-server.itlab.com) by using ssh, and install required packages using yum command.
yum install -y curl policycoreutils-pythonIt also requires postfix and openssh-server packages. But both of them are already installed with minimal installation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) or CentOS 7.6.
Allow the http service through Linux firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
firewall-cmd --reloadInstall GitLab package repository as follows.
curl https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ee/script.rpm.sh | bashOutput:
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 6463 0 6463 0 0 3729 0 --:--:-- 0:00:01 --:--:-- 3729
Detected operating system as rhel/7.
Checking for curl...
Detected curl...
Downloading repository file: https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ee/config_file.repo?os=rhel&dist=7&source=script
done.
Installing pygpgme to verify GPG signatures...
Loaded plugins: product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-manager
This system is not registered with an entitlement server. You can use subscription-manager to register.
gitlab_gitlab-ee-source/signature | 836 B 00:00
Retrieving key from https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ee/gpgkey
Importing GPG key 0xE15E78F4:
Userid : "GitLab B.V. (package repository signing key) "
Fingerprint: 1a4c 919d b987 d435 9396 38b9 1421 9a96 e15e 78f4
From : https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ee/gpgkey
Retrieving key from https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ee/gpgkey/gitlab-gitlab-ee-3D645A26AB9FBD22.pub.gpg
gitlab_gitlab-ee-source/signature | 951 B 00:01 !!!
gitlab_gitlab-ee-source/primary | 175 B 00:02
Package pygpgme-0.3-9.el7.x86_64 already installed and latest version
Nothing to do
Installing yum-utils...
Loaded plugins: product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-manager
This system is not registered with an entitlement server. You can use subscription-manager to register.
Package yum-utils-1.1.31-50.el7.noarch already installed and latest version
Nothing to do
Generating yum cache for gitlab_gitlab-ee...
Importing GPG key 0xE15E78F4:
Userid : "GitLab B.V. (package repository signing key) "
Fingerprint: 1a4c 919d b987 d435 9396 38b9 1421 9a96 e15e 78f4
From : https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ee/gpgkey
The repository is setup! You can now install packages.
Install GitLab on CentOS 7 as follows:
EXTERNAL_URL="http://gitlab-server.itlab.com" yum install -y gitlab-eeOutput:
Loaded plugins: product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-manager
This system is not registered with an entitlement server. You can use subscription-manager to register.
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package gitlab-ee.x86_64 0:11.5.3-ee.0.el7 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
gitlab-ee x86_64 11.5.3-ee.0.el7 gitlab_gitlab-ee 495 M
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 1 Package
Total download size: 495 M
Installed size: 1.4 G
Downloading packages:
warning: /var/cache/yum/x86_64/7Server/gitlab_gitlab-ee/packages/gitlab-ee-11.5.3-ee.0.el7.x86_64.rpm: Header V4 RSA/SHA1 Signature, key ID f27eab47: NOKEY
Public key for gitlab-ee-11.5.3-ee.0.el7.x86_64.rpm is not installed
gitlab-ee-11.5.3-ee.0.el7.x86_64.rpm | 495 MB 65:20
Retrieving key from https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ee/gpgkey
Importing GPG key 0xE15E78F4:
Userid : "GitLab B.V. (package repository signing key) "
Fingerprint: 1a4c 919d b987 d435 9396 38b9 1421 9a96 e15e 78f4
From : https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ee/gpgkey
Retrieving key from https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ee/gpgkey/gitlab-gitlab-ee-3D645A26AB9FBD22.pub.gpg
Importing GPG key 0xF27EAB47:
Userid : "GitLab, Inc. "
Fingerprint: dbef 8977 4ddb 9eb3 7d9f c3a0 3cfc f9ba f27e ab47
From : https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ee/gpgkey/gitlab-gitlab-ee-3D645A26AB9FBD22.pub.gpg
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : gitlab-ee-11.5.3-ee.0.el7.x86_64 1/1
...
...
...
Running handlers:
Running handlers complete
Chef Client finished, 457/672 resources updated in 18 minutes 23 seconds
gitlab Reconfigured!
*. *.
*** ***
***** *****
.****** *******
******** ********
,,,,,,,,,***********,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,*********,,,,,,,,,,,
.,,,,,,,,,,,*******,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,*****,,,,,,,,,.
,,,,,,,****,,,,,,
.,,,***,,,,
,*,.
_______ __ __ __
/ ____(_) /_/ / ____ _/ /_
/ / __/ / __/ / / __ `/ __
/ /_/ / / /_/ /___/ /_/ / /_/ /
____/_/__/_____/__,_/_.___/
Thank you for installing GitLab!
GitLab should be available at http://gitlab-server.itlab.com
For a comprehensive list of configuration options please see the Omnibus GitLab readme
https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/omnibus-gitlab/blob/master/README.md
Verifying : gitlab-ee-11.5.3-ee.0.el7.x86_64 1/1
Installed:
gitlab-ee.x86_64 0:11.5.3-ee.0.el7
Complete!
GitLab EE (Enterprise Edition) has been installed on our Linux system.
Configure GitLab Server
Browse the URL http://gitlab.itlab.com using a client’s browser.
Since, we are login for the first time on our GitLab Server , therefore, we need to set the GitLab password for root user.
After Setting GitLab Password, we are redirected to the GitLab Server Login Page.
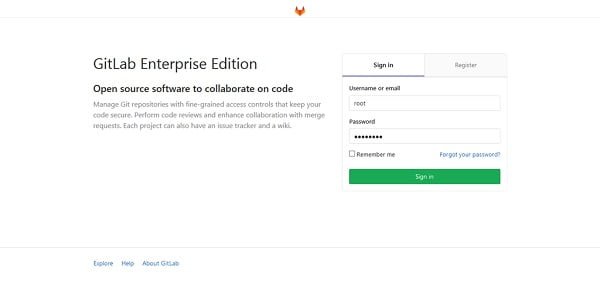
Sign-in to GitLab Server using new password.
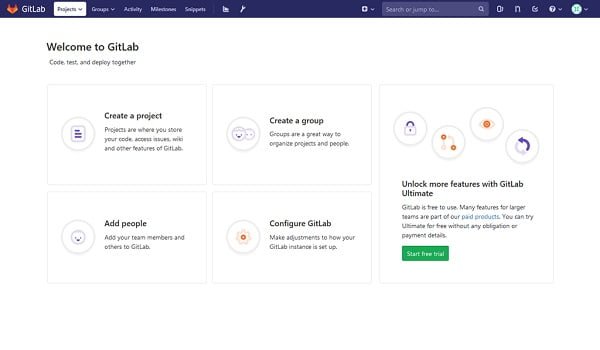
Now, we are connected with our GitLab server.
Acer Chromebook Plus 514 User Guide: Step-by-Step Instructions for Setup, Customization, and Maximizing Productivity
$16.99 (as of July 9, 2025 21:12 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Final Thoughts
By installing GitLab on CentOS 7, you’ve taken a major step toward full control of your development workflow, from source code management to CI/CD. With just a few setup steps—adding the repository, installing packages, and configuring the system—you now have a powerful self-hosted DevOps platform at your fingertips.
Don’t wait until service limits or outages impact your productivity—join the thousands of teams who already use GitLab to streamline collaboration and boost delivery speed. Start managing your code your way—securely, efficiently, and independently.
Optimize your cloud infrastructure and secure your servers with my AWS and Linux administration services. Let’s ensure your systems run smoothly. Connect with me on Fiverr now!
Thank you for reading, and happy developing with GitLab!



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.