Learn how to install GitLab on CentOS 8 with our step-by-step guide. Set up dependencies, configure repositories, and deploy GitLab for efficient source code management and DevOps automation. #centlinux #linux #git
Table of Contents
What is GitLab?
GitLab is a web-based DevOps lifecycle tool that provides a Git repository manager along with a comprehensive suite of features for software development and collaboration. It offers a centralized platform where teams can manage code repositories, plan and track project tasks, collaborate on code, and automate software delivery pipelines.
Key features of GitLab include:
- Git Repository Management: GitLab serves as a Git repository hosting service, allowing teams to store, manage, and version control their codebases.
- Issue Tracking and Project Management: It includes robust issue tracking capabilities with customizable issue boards, milestones, and labels. Teams can manage tasks, track progress, and coordinate efforts efficiently.
- CI/CD Pipelines: GitLab provides built-in Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) capabilities. Users can automate testing, building, and deploying applications, streamlining the software delivery process.
- Code Review: Facilitates code collaboration and review with features like merge requests (pull requests), inline commenting, and approvals, ensuring code quality and team collaboration.
- Wiki and Documentation: Offers a built-in wiki system for documenting projects and processes, enhancing knowledge sharing within teams.
- Security and Compliance: Includes security scanning tools to detect vulnerabilities in code and dependencies. GitLab also supports compliance features for managing access controls and auditing.
- Integration and Extensibility: Integrates with various third-party tools and services, allowing teams to customize their development workflows. It supports integrations with chat tools, issue trackers, monitoring systems, and more.
- Community and Enterprise Editions: GitLab is available in both Community Edition (CE), which is open-source and free to use, and Enterprise Edition (EE) with additional features and support for enterprise-grade deployments.
GitLab is popular among development teams for its comprehensive feature set, flexibility, and support for the entire DevOps lifecycle from planning to monitoring. Whether used by small teams or large enterprises, GitLab helps streamline collaboration, improve productivity, and accelerate software delivery.

GitLab vs GitHub
GitLab and GitHub are both widely used platforms for managing Git repositories and supporting collaborative software development, but they have distinct features and target audiences:
GitHub
Community and Open Source Focus:
- GitHub is renowned for its strong community of open-source developers and projects.
- It’s often used for hosting public repositories and contributing to open-source software.
User Interface and Integration:
- Known for its intuitive and user-friendly interface, GitHub simplifies code hosting, collaboration, and code review processes.
- Offers seamless integration with various third-party services and tools, enhancing its versatility in development workflows.
Social Coding and Collaboration:
- Emphasizes social coding features such as pull requests, issue tracking, and project boards.
- Facilitates community collaboration through discussions, forks, and contributions to public repositories.
Marketplace and Ecosystem:
- GitHub Marketplace provides a range of integrations and tools for developers, enhancing productivity and project management capabilities.
- Supports a broad ecosystem of plugins, extensions, and integrations that extend its functionality.
Enterprise Solutions:
- GitHub offers GitHub Enterprise, a self-hosted version with additional security, compliance, and management features tailored for enterprise use.
GitLab
Integrated DevOps Platform:
- GitLab positions itself as a complete DevOps platform with built-in CI/CD pipelines, code review, issue tracking, and more.
- Provides a unified experience for planning, managing, and deploying software projects.
Built-in CI/CD:
- GitLab includes robust Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) capabilities directly integrated into the platform.
- Enables automated testing, building, and deploying of applications without relying on external services.
Customization and Flexibility:
- Offers extensive customization options and flexibility, supporting self-hosted deployments and allowing organizations to tailor the platform to their needs.
- Provides features like customizable workflows, group-level permissions, and extensive API support for integration with other tools.
Security and Compliance:
- Focuses on security with built-in security scanning tools, compliance features, and role-based access controls.
- Suitable for organizations with stringent security and compliance requirements.
Community and Enterprise Editions:
- GitLab is available in both Community Edition (CE), which is open-source, and Enterprise Edition (EE) with additional features and enterprise-grade support.
Summary
- GitHub is ideal for open-source projects, community-driven development, and teams looking for a user-friendly interface with strong social coding features.
- GitLab is suited for organizations and teams seeking an integrated DevOps platform with built-in CI/CD, extensive customization options, and robust security features.
Choosing between GitHub and GitLab depends on factors such as project scope, team size, desired integration capabilities, and preferences for self-hosting versus cloud-based solutions. Both platforms excel in their respective strengths, catering to a wide range of development workflows and collaboration needs.
Linux Server Specification
We are using a minimal installed CentOS 8 virtual machine with following specification.
- CPU – 3.4 Ghz (2 cores)
- Memory – 2 GB
- Storage – 40 GB
- Operating System – CentOS 8.2
- Hostname – gitlab-ce-01.centlinux.com
- IP Address – 192.168.116.206 /24
For a smooth GitLab installation and optimal performance on CentOS 8, it’s recommended to have a system with at least 4 GB of RAM, 2 CPU cores, and 20 GB of free disk space.
If you’re experimenting with Linux server setups or want a dedicated environment for GitLab without affecting your main workstation, consider using a compact Mini PC or a reliable VPS like Rose Hosting.
Both options provide affordable, scalable solutions ideal for testing and development. Using a Mini PC offers you a physical device under your control, while a VPS provides flexibility with remote server management.
If you’re interested, check out the Mini PCs and Rose Hosting VPS options linked below to get started quickly and efficiently.
[Grab a Mini PC for your Home Lab – Shop with Us!]
[Launch Your Own VPS with Rose Hosting – Click to Get Started!]
Disclosure: These are affiliate links, and I may earn a commission at no extra cost to you if you purchase through them.
Update your Linux Server
Connect with gitlab-ce-01.centlinux.com as root user by using PuTTY.
Update installed software packages by using dnf command.
dnf update -yVerify the Linux Kernel version.
uname -aOutput:
Linux gitlab-ce-01.centlinux.com 4.18.0-193.6.3.el8_2.x86_64 #1 SMP Wed Jun 10 11:09:32 UTC 2020 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
Verify the version of Linux operating system.
cat /etc/redhat-releaseOutput:
CentOS Linux release 8.2.2004 (Core)
Install GitLab Prerequisites
GitLab requires some other software packages. Therefore, we are installing them by using the dnf command.
dnf install -y curl policycoreutils openssh-serverAll three packages are already installed on our Linux server.
DevOps software also requires a local SMTP server to send emails notifications. Therefore, we are installing Postfix on our Linux server.
dnf install -y postfixStart and enable Postfix service.
systemctl enable --now postfix.serviceConfigure Linux Firewall
GitLab web application runs by default on port 80 and 443. Therefore, we are allowing the http and https services in Linux firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service={http,https}
firewall-cmd --reloadInstall GitLab Yum Repository
GitLab documentation provides a script to to install their official yum repository. We are executing that same command here.
curl https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/script.rpm.sh | sudo bashInstall GitLab on CentOS 8
Since, we have successfully installed GitLab yum repository on our CentOS 8 machine. Now, we can easily install our DevOps Server by using dnf command.
dnf install -y gitlab-ceGitLab CE installation has been successful.
GitLab Server Configuration
GitLab server configuration files are located in /etc/gitlab directory.
Open gitlab.rb configuration file in a text editor.
vi /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rbLocate and set external_url directive as follows.
external_url 'http://gitlab-ce-01.centlinux.com'Invoke the GitLab server configuration process by using the following command. You should keep patience, because it will take a while to complete. On machine that was used in this tutorial, it took about 44 minutes to complete.
gitlab-ctl reconfigureOutput:
Starting Chef Client, version 14.14.29
resolving cookbooks for run list: ["gitlab"]
Synchronizing Cookbooks:
- gitlab (0.0.1)
- redis (0.1.0)
- mattermost (0.1.0)
- gitaly (0.1.0)
- praefect (0.1.0)
- letsencrypt (0.1.0)
- package (0.1.0)
- postgresql (0.1.0)
- consul (0.1.0)
- registry (0.1.0)
- monitoring (0.1.0)
- runit (5.1.3)
- nginx (0.1.0)
- crond (0.1.0)
- acme (4.1.1)
Installing Cookbook Gems:
Compiling Cookbooks...
...
...
...
Running handlers:
Running handlers complete
Chef Client finished, 562/1517 resources updated in 44 minutes 21 seconds
gitlab Reconfigured!
Access GitLab Web Interface
GitLab is web-based, therefore, we only requires a supported web browser to access the application.
Open URL http://gitlab-ce-01.centlinux.com in a web browser.
Since, we are accessing GitLab web interface for the first time, therefore, we have been asked by the application to set a strong administrator password.
Default administrative user is root.
Set a strong password for the root user.
Now, sign-in to web application as root user.
We have reached the main screen of the web application.
Click on “Configure GitLab”.
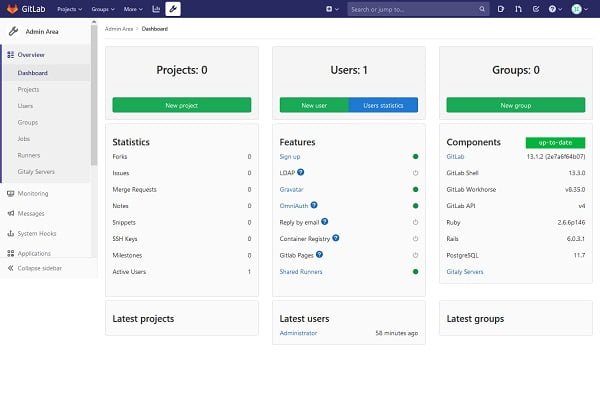
We have been redirected to the Dashboard of the GitLab web interface. You can confirm the versions of GitLab components that have been installed on our Linux server.
Let’s enhance your development process together!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is GitLab, and why is it used?
GitLab is a web-based DevOps platform that provides Git repository management, CI/CD pipelines, issue tracking, and collaboration tools for software development teams.
What are the prerequisites for installing GitLab on CentOS 8?
Before installing GitLab, ensure that your system has at least 4GB of RAM, a supported CPU, and that Postfix or another mail server is installed for email notifications.
Why do I need to configure a firewall for GitLab?
GitLab uses HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443) for web access and SSH (port 22 or a custom port) for Git repository access. Configuring the firewall ensures proper accessibility and security.
What are the key configuration steps after installing GitLab?
After installation, you need to set up an admin password, configure external URL settings, enable SSL for security, and fine-tune performance settings based on your workload.
How do I access GitLab after installation?
Once installed and started, GitLab can be accessed through a web browser using your server’s IP address or domain name, where you can log in and start managing repositories.
Final Thoughts
Installing GitLab on CentOS 8 enables you to create a powerful self-hosted Git repository and DevOps platform for managing source code, CI/CD pipelines, and team collaboration.
By following the installation steps, configuring the necessary dependencies, and setting up your GitLab instance, you can efficiently manage projects and streamline software development. Once installed, ensure proper firewall and SSL configurations for enhanced security and optimal performance.
From setting up scalable AWS solutions to managing complex Linux environments, I’ve got you covered. Visit my Freelancer profile to get started.
Recommended Courses
If you’re just starting your journey into DevOps, GitLab CI/CD: Pipelines, CI/CD and DevOps for Beginners by Valentin Despa is an excellent hands-on course to build a strong foundation. It covers everything from the basics of pipelines to practical CI/CD workflows, helping you master automation and streamline your software delivery process. Whether you’re a developer, sysadmin, or aspiring DevOps engineer, this course gives you the step-by-step guidance you need to become confident with GitLab CI/CD.
Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links. If you purchase through these links, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.