Learn how to install LEMP Stack on RHEL 8 with our step-by-step guide. Follow detailed instructions to set up and configure your LEMP Stack for optimal performance on RHEL 8. #centlinux #linux #nginx #mysql #php
Table of Contents
What is LEMP Stack?
LEMP is a popular software stack. LEMP is named after the first letter of four software that forms the Stack i.e. Linux, Nginx, MySQL and PHP. LEMP is used to deploy PHP based web applications with MySQL database backend. LEMP is a variation of original LAMP stack, where Apache HTTP Server is replaced by Nginx Web Server.
The LEMP Stack is a popular open-source software stack used for creating and managing web applications. It’s an acronym that stands for:
LEMP Stack Components
- Linux:
- Role: The operating system for the stack. It provides a stable and secure environment for running web applications.
- Features: Open-source, highly customizable, robust security features, and strong community support.
- Nginx:
- Role: The web server and reverse proxy server. It handles HTTP requests, serves static content, and forwards dynamic content requests to PHP.
- Features: High performance, low resource usage, scalable, and capable of handling a large number of concurrent connections.
- MySQL/MariaDB:
- Role: The relational database management system (RDBMS) used to store and manage application data.
- Features: MySQL is known for its speed and reliability, while MariaDB, a MySQL fork, offers additional features and enhancements. Both support complex queries, transactions, and large datasets.
- PHP:
- Role: The server-side scripting language used for creating dynamic web content and applications.
- Features: Widely used for web development, integrates easily with HTML, and has a large ecosystem of libraries and frameworks.

Advantages of the LEMP Stack
- Performance: Nginx is known for its efficiency and high performance, especially for handling high traffic loads. PHP processes dynamic content, while MySQL/MariaDB handles data management tasks.
- Scalability: The stack components are designed to scale horizontally to accommodate increasing traffic and data requirements.
- Flexibility: The components are highly configurable and can be customized to meet specific needs and preferences.
- Security: Linux and Nginx offer strong security features, while MySQL/MariaDB provides options for data protection and access control.
- Cost-Effective: All components of the LEMP Stack are open-source and free to use, making it a cost-effective solution for web hosting.
- Community Support: Each component has a large and active community, offering extensive resources for troubleshooting and optimization.
Common Use Cases for the LEMP Stack
- Web Hosting: Ideal for hosting websites and web applications of various sizes.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Supports popular CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
- E-Commerce Platforms: Suitable for building and managing online stores and e-commerce solutions.
- Custom Web Applications: Provides a foundation for developing and deploying custom web applications with dynamic features.
In this article, we will install LEMP stack on RHEL 8 server. To achieve this goal, we are installing MariaDB database, Nginx web server and PHP language support on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8 server.
Recommended Training: Introduction to NGINX from Hussein Nasser

Environment Specification
We have installed a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8 virtual machine with following specifications.
- CPU – 3.4 Ghz (2 cores)
- Memory – 2 GB
- Storage – 20 GB
- Hostname – rhel-8-lemp.example.com
- IP Address – 192.168.116.165/24
- Operating System – Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8
We have also configured a Local YUM repository on our RHEL 8 server, so we can install required software without an active Red Hat subscription.
Install MariaDB on RHEL 8
Connect with rhel-8-lemp.example.com using ssh as root user.
MariaDB Server 10.3 is available in RHEL 8 local AppStream repository. Therefore, we can install it easily using dnf command.
dnf install -y mariadb-serverEnable and start MariaDB service.
systemctl enable mariadb.service
systemctl start mariadb.serviceConfigure and secure MariaDB database instance.
mysql_secure_installationOutput:
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] Y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
AULA WIN68 HE Mechanical Gaming Keyboard 60%, Hall Effect Magnetic Switch, Fast Trigger Mode Adjustable Actuation, 8000Hz Polling Rate, RGB Backlit Wired Keyboard for Laptop/PC Gamer
$39.99 (as of July 6, 2025 20:00 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Install Nginx on RHEL 8
Nginx 1.14 is available in local AppStream repository. Therefore, we can install it using dnf command.
yum install -y nginxEnable and start Nginx service.
systemctl enable nginx.service
systemctl start nginx.serviceAllow HTTP service in Linux firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
firewall-cmd --reloadOpen URL http://rhel-8-lemp.example.com in a client’sweb browser.
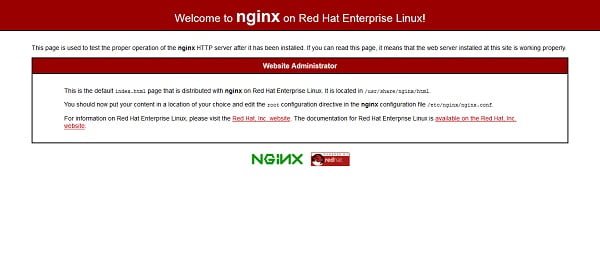
Nginx web server is installed and working fine on our Linux server.
Install PHP on RHEL 8
PHP 7.2 is available in local AppStream repository. Therefore, we can install it using dnf command.
dnf install -y php php-mysqlnd php-pdo php-gd php-mbstring php-fpmEdit php-fpm configurations.
vi /etc/php-fpm.d/www.confFind and set following settings therein.
user = nginx
group = nginx
listen.owner = nginx
listen.group = nginxStart and enable php-fpm service.
systemctl enable php-fpm.service
systemctl start php-fpm.serviceRestart Nginx service to integrate PHP with Nginx.
systemctl restart nginx.serviceCreate a PHP file to check information about installed PHP modules.
echo "<?php phpinfo() ?>" > /usr/share/nginx/html/info.phpOpen URL http://rhel-8-lemp.example.com/info.php in a web browser.
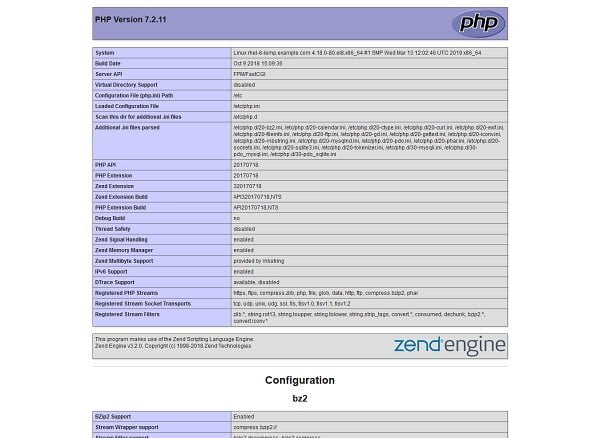
PHP 7.2 has been installed and running on our Linux server.
Read Also: How to install LEMP on Ubuntu 14
Linux Basics for Hackers: Getting Started with Networking, Scripting, and Security in Kali
$20.99 (as of July 7, 2025 20:55 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Final Thoughts
Installing the LEMP stack (Linux, Nginx, MariaDB, and PHP) on RHEL 8 gives you a high-performance platform for hosting modern, dynamic web applications. In this guide, we walked through installing and configuring each component to work together efficiently.
With your LEMP stack now up and running, you have a lightweight, secure, and scalable environment ready for development and production use. To ensure optimal performance and security, remember to apply regular updates, monitor your services, and follow best practices for server and application management.
Looking for a Linux server expert? I provide top-tier administration, performance tuning, and security solutions for your Linux systems. Explore my Fiverr profile for details!



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.