Learn how to install Netdata on RHEL 8 with this comprehensive guide. Follow step-by-step instructions to set up real-time performance monitoring and troubleshooting for your system. #centlinux #linux #netdata
Table of Contents
What is Netdata?
Netdata is a powerful, open-source monitoring and troubleshooting tool designed to provide real-time insights into the performance and health of systems and applications. It offers comprehensive monitoring capabilities for a wide range of metrics, including CPU usage, memory, disk I/O, network traffic, and application-specific data. (Netdata Official Website)
Key Features of Netdata:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Netdata collects and visualizes metrics in real-time, allowing users to identify and respond to issues as they occur.
- Comprehensive Metrics: It monitors a wide array of system and application metrics, providing a holistic view of performance.
- Interactive Dashboards: Netdata provides highly interactive and customizable web-based dashboards that allow users to drill down into specific metrics and time frames.
- Lightweight and Efficient: Despite its extensive monitoring capabilities, Netdata is designed to be lightweight and have minimal impact on system performance.
- Alerts and Notifications: Users can configure alerts to be notified of performance issues, with support for various notification channels.
- Scalability: Netdata can be used to monitor single nodes or scaled to monitor complex, distributed infrastructures.
- Open-Source and Extensible: As an open-source tool, Netdata is highly extensible and supported by a community of developers and users.
Being an Open Source Monitoring Dashboard, Netdata is particularly useful for system administrators, developers, and IT professionals who need to ensure the optimal performance and reliability of their systems and applications. It provides the visibility and insights necessary to troubleshoot issues quickly and maintain high levels of service uptime.
Netdata Alternatives
There are several alternatives to Netdata, each offering various features and capabilities for monitoring and troubleshooting systems and applications. Here are some popular options:
Prometheus
- Description: An open-source systems monitoring and alerting toolkit originally built at SoundCloud.
- Features: Strong data collection capabilities, powerful query language (PromQL), integration with Grafana for visualization, extensive community and ecosystem support.
- Use Case: Ideal for large-scale monitoring, time-series data collection, and alerting.
Grafana
- Description: An open-source platform for monitoring and observability.
- Features: Highly customizable dashboards, support for multiple data sources (including Prometheus, InfluxDB, Graphite), alerting, plugins for extended functionality.
- Use Case: Best for creating complex, interactive dashboards and visualizations.
Zabbix
- Description: An open-source monitoring software for networks and applications.
- Features: Extensive monitoring capabilities, robust alerting and notification system, scalability, built-in support for various data collection methods.
- Use Case: Suitable for network monitoring, infrastructure monitoring, and application performance monitoring.
Nagios
- Description: A widely used open-source monitoring system.
- Features: Comprehensive monitoring of applications, services, and infrastructure, strong alerting and notification, plugins for extended functionality, customizable monitoring setup.
- Use Case: Ideal for monitoring critical systems and ensuring high availability.
Datadog
- Description: A cloud-based monitoring and analytics platform.
- Features: Real-time monitoring, application performance monitoring (APM), log management, infrastructure monitoring, integrations with various services and technologies.
- Use Case: Best for organizations using cloud services and needing integrated monitoring and analytics.
New Relic
- Description: A cloud-based observability platform.
- Features: Application performance monitoring, infrastructure monitoring, real-time analytics, integrated logs, alerts, and dashboards.
- Use Case: Suitable for full-stack observability and performance optimization.
InfluxDB
- Description: An open-source time-series database developed by InfluxData.
- Features: High performance for time-series data, powerful query language (Flux), integration with visualization tools like Grafana, extensive ecosystem.
- Use Case: Ideal for time-series data storage and analysis, IoT data collection.
Sensu
- Description: An open-source monitoring solution for dynamic environments.
- Features: Scalable and extensible, supports custom checks and plugins, integrates with other monitoring and alerting systems.
- Use Case: Suitable for cloud-native environments, DevOps monitoring, and event-driven monitoring.
Each of these tools has its strengths and ideal use cases, so the best choice depends on your specific monitoring needs, infrastructure, and preferred workflows.
Environment Specification
We are using a minimal Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 virtual machine with following specifications.
- CPU – 3.4 Ghz (2 cores)
- Memory – 2 GB
- Storage – 20 GB
- Operating System – Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.5
- Hostname – netdata-01.centlinux.com
- IP Address – 192.168.116.243 /24
For setting up your Netdata monitoring environment on RHEL 8, having a reliable and efficient platform is essential. Many Linux enthusiasts and professionals prefer using a Mini PC or a VPS service like Hostinger for their home lab setups. A Mini PC offers a compact, energy-efficient, and always-on hardware solution that is perfect for running continuous monitoring tools like Netdata.
[Power Your Projects with the Best Mini PC – Shop Now!]
Alternatively, a Hostinger VPS provides scalable and accessible cloud resources, ideal for remote management and experimentation without the need for physical hardware.
[Discover the Power of Rose Hosting VPS – Limited Time Offer!]
Both options are excellent for hands-on Linux server practice, testing configurations, and monitoring in real-time, helping you build a versatile home lab environment that supports learning and development.
Disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links. If you purchase through these links, we may earn a commission at no extra cost to you, which helps support the blog and our content creation efforts.
Update your Linux Server
By using a ssh client, connect with netdata-01.centlinux.com as root user.
Rebuild cache of enabled yum repositories.
dnf makecacheUpdate your Linux operating system by executing following command.
dnf update -yThe above command may updates your Linux Kernel. In this case, you should reboot your Linux server with newly installed Linux Kernel.
rebootCheck the Linux operating system and Kernel versions.
uname -r
cat /etc/os-releaseOutput:
4.18.0-348.12.2.el8_5.x86_64
NAME="Red Hat Enterprise Linux"
VERSION="8.5 (Ootpa)"
ID="rhel"
ID_LIKE="fedora"
VERSION_ID="8.5"
PLATFORM_ID="platform:el8"
PRETTY_NAME="Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.5 (Ootpa)"
ANSI_COLOR="0;31"
CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:redhat:enterprise_linux:8::baseos"
HOME_URL="https://www.redhat.com/"
DOCUMENTATION_URL="https://access.redhat.com/documentation/red_hat_enterprise_linux/8/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugzilla.redhat.com/"
REDHAT_BUGZILLA_PRODUCT="Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8"
REDHAT_BUGZILLA_PRODUCT_VERSION=8.5
REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT="Red Hat Enterprise Linux"
REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT_VERSION="8.5"
Read Also: How to upgrade RHEL 9 to RHEL 10
Install Third Party Yum Repositories
Netdata software requires some packages that are not available in standard yum repositories. Therefore, you are required to install a few third party yum repositories on your Linux server.
First of all, install EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) yum repository by executing following command.
dnf install -y https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpmYou also need to enable PowerTools repository.
For CentOS / Rocky Linux you can execute following command to enable PowerTools repository.
dnf install -y 'dnf-command(config-manager)'
dnf -y config-manager --set-enabled PowerToolsWhereas, for RHEL, execute the following command.
subscription-manager repos --enable codeready-builder-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpmsOutput:
1 local certificate has been deleted.
Repository 'codeready-builder-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms' is enabled for this system.
Build cache for newly installed yum repositories.
You may also required to add Okay yum repository, Because some of the Netdata required packages are provided thereby.
dnf install -y http://repo.okay.com.mx/centos/8/x86_64/release/okay-release-1-3.el8.noarch.rpmAfter installing Okay repository, you may need to edit the okay.repo file to make it usable.
Edit okay.repo by using vim text editor.
vi /etc/yum.repos.d/okay.repoLocate following lines therein.
failovermethod=priority
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-OKAYAnd amend them as follows.
#failovermethod=priority
gpgcheck=0
#gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-OKAYRemove any cached packages from the Linux operating system.
dnf clean packagesOutput:
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
89 files removed
Update Okay repository as follows.
dnf update -y okay-releaseEdit the okay.repo file again. Because, the update process also remove the changes that you have made in previous steps.
vi /etc/yum.repos.d/okay.repoLocate and comment following directive in this file.
#failovermethod=priorityBuild cache for newly installed yum repositories.
dnf makecacheOutput:
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 8 - x86_64 32 kB/s | 18 kB 00:00
Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux Modular 8 - 32 kB/s | 18 kB 00:00
Extra OKay Packages for Enterprise Linux - x86_ 150 kB/s | 4.3 MB 00:29
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 for x86_64 - BaseOS 4.4 kB/s | 4.1 kB 00:00
Red Hat CodeReady Linux Builder for RHEL 8 x86_ 3.3 kB/s | 4.5 kB 00:01
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 for x86_64 - AppStre 6.1 kB/s | 4.5 kB 00:00
Install Netdata Prerequisites
Since, you have already setup the required yum repositories, therefore, you can easily install Netdata prerequisites packages on your Linux server by executing following command.
dnf install -y autoconf automake curl gcc git cmake libuuid-devel openssl-devel libuv-devel lz4-devel make nc pkgconfig python3 zlib-devel gcc-c++ libbpf-develNetdata also requires Judy-devel package from Okay yum repository. But it’s installation is little bit tricky.
Judy is a dependency of Judy-devel package. But an older version of Judy package is also available in Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) Appstream repository.
Therefore, you need to disable the RHEL Appstream before install Judy-devel package.
subscription-manager repos --disable rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpmsOutput:
Repository 'rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms' is disabled for this system.
Now install Judy-devel package as follows.
dnf install -y Judy-develAfter successful installation of Judy-devel, enable the RHEL Appstream again.
subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpmsOutput:
Repository 'rhel-8-for-x86_64-appstream-rpms' is enabled for this system.
Install Netdata on RHEL 8
Netdata is available to download at GitHub. Therefore, execute git command to clone Netdata repository.
cd
git clone https://github.com/netdata/netdata.git --depth=100 --recursiveThe Netdata software has been downloaded into netdata directory.
Now execute the Netdata installation script with following command switches, to install Netdata on RHEL 8 server.
cd netdata
./netdata-installer.sh --stable-channel --dont-wait --install /optOutput:
^
|.-. .-. .-. .-. . netdata
| '-' '-' '-' '-' real-time performance monitoring, done right!
+----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+--->
You are about to build and install netdata on CentOS Linux.
The build process will use /tmp for
any temporary files. You can override this by setting $TMPDIR to a
writable directory where you can execute files.
It will be installed at these locations:
- the daemon at /opt/netdata/usr/sbin/netdata
- config files in /opt/netdata/etc/netdata
- web files in /opt/netdata/usr/share/netdata
- plugins in /opt/netdata/usr/libexec/netdata
- cache files in /opt/netdata/var/cache/netdata
- db files in /opt/netdata/var/lib/netdata
- log files in /opt/netdata/var/log/netdata
- pid file at /opt/netdata/var/run/netdata.pid
- logrotate file at /etc/logrotate.d/netdata
This installer allows you to change the installation path.
Press Control-C and run the same command with --help for help.
NOTE:
Anonymous usage stats will be collected and sent to Netdata.
To opt-out, pass --disable-telemetry option to the installer or export
the environment variable DO_NOT_TRACK to a non-zero or non-empty value
(e.g: export DO_NOT_TRACK=1).
...
...
...
Memory de-duplication instructions
You have kernel memory de-duper (called Kernel Same-page Merging,
or KSM) available, but it is not currently enabled.
To enable it run:
echo 1 >/sys/kernel/mm/ksm/run
echo 1000 >/sys/kernel/mm/ksm/sleep_millisecs
If you enable it, you will save 40-60% of netdata memory.
--- Check version.txt ---
--- Check apps.plugin ---
--- Copy uninstaller ---
--- Basic netdata instructions ---
netdata by default listens on all IPs on port 19999,
so you can access it with:
http://this.machine.ip:19999/
To stop netdata run:
systemctl stop netdata
To start netdata run:
systemctl start netdata
Uninstall script copied to: /opt/netdata/usr/libexec/netdata/netdata-uninstaller.sh
--- Installing (but not enabling) the netdata updater tool ---
Failed to disable unit: Unit file netdata-updater.timer does not exist.
Update script is located at /opt/netdata/usr/libexec/netdata/netdata-updater.sh
--- Check if we must enable/disable the netdata updater tool ---
You chose *NOT* to enable auto-update, removing any links to the updater from cron (it may have happened if you are reinstalling)
--- Wrap up environment set up ---
Preparing .environment file
[/root/netdata]# chmod 0644 /opt/netdata/etc/netdata/.environment
OK
Setting netdata.tarball.checksum to 'new_installation'
--- We are done! ---
^
|.-. .-. .-. .-. .-. . netdata .-. .-
| '-' '-' '-' '-' '-' is installed and running now! -' '-'
+----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+--->
enjoy real-time performance and health monitoring...
Netdata software has been installed and the relevant network services has been started by the installation process.
Read Also: LibreNMS Oxidized Integration Guide
Configure Linux Firewall
Netdata software uses default service port 19999/tcp. Therefore, you may need to allow this port in Linux firewall to make it accessible across the network.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=19999/tcp
firewall-cmd --reloadAccess Netdata: Open Source Monitoring Dashboard
Open URL http://netdata-01.centlinux.com:19999 in a web browser.
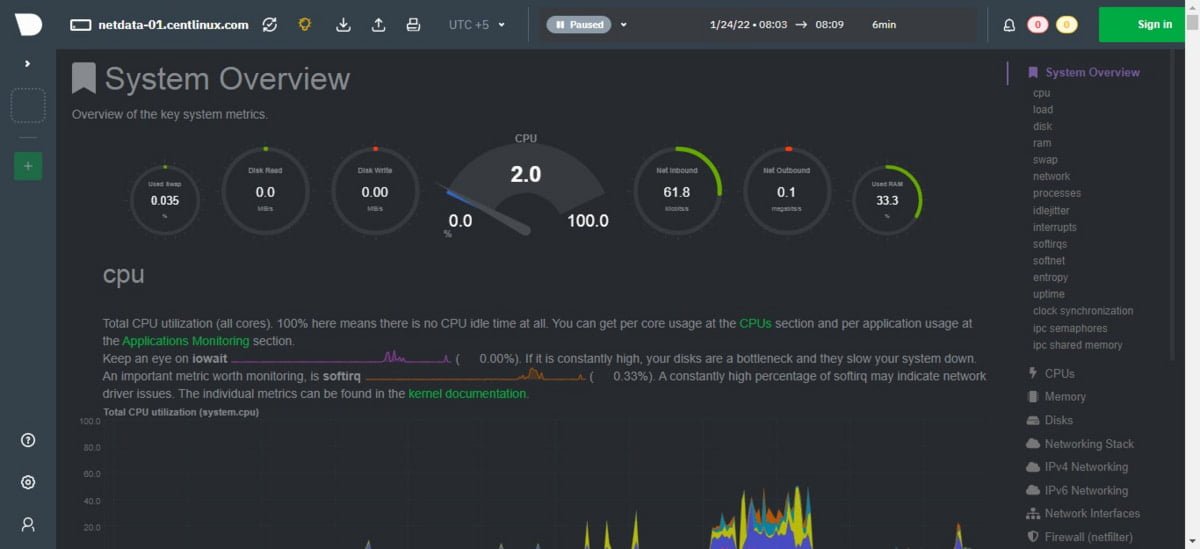
You have reached at the dashboard of Netdata web application. It is now showing the performance statistics of your Linux server.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Netdata installation on RHEL 8 is a straightforward process that provides powerful real-time monitoring capabilities for your system. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can quickly set up Netdata and gain valuable insights into your system’s performance and health.
Struggling with Linux server management? I offer professional support to ensure your servers are secure, optimized, and always available. Visit my Freelancer profile to learn more!
FAQs
Q1: Can Netdata run on a minimal RHEL 8 server without a GUI?
Yes, Netdata is designed to run on minimal servers and does not require a graphical user interface to monitor system metrics.
Q2: Does installing Netdata affect server performance on RHEL 8?
Netdata uses very low system resources and runs efficiently in the background, so it has minimal impact on server performance.
Q3: How can I secure access to the Netdata dashboard on RHEL 8?
You can secure Netdata by enabling SSL, setting up authentication, or using firewall rules to restrict access.
Q4: Is it possible to customize the Netdata monitoring dashboard on RHEL 8?
Yes, Netdata allows customization of its dashboard via configuration files for tailored monitoring visuals.
Q5: Which dependencies are essential before installing Netdata on RHEL 8?
Make sure wget, curl, gcc, and make are installed; these are commonly required for building and installing Netdata.
Recommended Courses
If you’re serious about mastering IT infrastructure monitoring, the Zabbix Application and Network Monitoring by Sean Bradley course is a must-have resource. This practical training walks you through real-world scenarios to monitor servers, applications, and networks with confidence, making it ideal for system administrators, DevOps engineers, and IT professionals aiming to level up their skills. By enrolling, you’ll gain hands-on knowledge that can save countless hours in troubleshooting and system management. [Click here to check out the course]
Disclaimer: This link is an affiliate link, which means I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you if you decide to purchase through it. This helps support my blog and allows me to continue creating useful content.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.