Learn how to install Portainer on CentOS 7 with our step-by-step guide. Follow detailed instructions for a smooth and effective Portainer setup to manage your Docker environments. #centlinux #linux #docker
Table of Contents
What is Portainer?
Portainer is a web-based user interface for management of Docker environments. It is free and open-source management toolset that allows us to easily build, manage and maintain Containerized environments. Portainer gives us a detailed overview of our Docker Cluster and allows us to manage our containers, images, networks, volumes, registries, services, nodes and stacks from a single web interface.
Requirement of a Web UI arises because Docker Engine CE provides a single CLI utility (i.e. docker) to create and manage all components of the Docker environments. It is good for hardcore CLI DevOps engineers, but it is quiet difficult for GUI addicts. Therefore, we have to look for some third party Web UI like Portainer to help the non-CLI users in performing the same tasks from an Web UI.
In this article, we are install Portainer on CentOS 7. To achieve this we use the container technology, as we download Portainer image from Docker Hub and run it to manage our Docker Swarm cluster.

System Specification
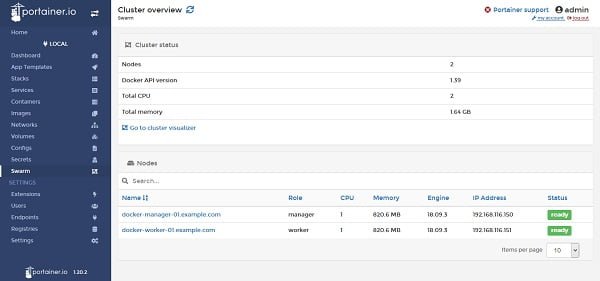
We have a Docker Swarm cluster on CentOS 7 consist of two nodes (1 Manager & 1 Worker) with following specifications:
| Hostname: | docker-manager-01 | docker-worker-01 |
| IP Address: | 192.168.116.150/24 | 192.168.116.151/24 |
| Operating System: | CentOS 7.6 | CentOS 7.6 |
| Docker Version: | Docker CE 18.09 | Docker CE 18.09 |
| Node Role: | Manager | Worker |
To setup the required environment, you can refer to our previous article Configure Docker Swarm Cluster on CentOS 7.
If you’re serious about mastering modern containerization and orchestration, Docker and Kubernetes: The Complete Guide by Stephen Grider is a must-have course. Designed for beginners and professionals alike, it walks you step-by-step through building, deploying, and scaling applications with Docker and Kubernetes—the two most in-demand technologies in DevOps today. With practical projects and expert explanations, this course can fast-track your skills and career growth.
Disclaimer: This link is an affiliate link, and I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you if you decide to enroll through it.
Install Portainer on CentOS 7
Connect to Docker Swarm’s Manager node docker-manager-01 using ssh as root user.
List the nodes in our Docker Swarm cluster.
docker node lsOutput:
ID HOSTNAME STATUS AVAILABILITY MANAGER STATUS ENGINE VERSION
3b9wynaya1wu910nf01m5jeeq * docker-manager-01.example.com Ready Active Leader 18.09.3
ydgqdyoksx2mb0snhe1hwvco7 docker-worker-01.example.com Ready Active
Pull the latest Portainer image from Portainer repository at Docker Hub.
docker pull portainer/portainer:latestOutput:
latest: Pulling from portainer/portainer
d1e017099d17: Pull complete
0b1e707a06d2: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:d6cc2c20c0af38d8d557ab994c419c799a10fe825e4aa57fea2e2e507a13747d
Status: Downloaded newer image for portainer/portainer:latest
Create a Docker volume for Portainer container data.
docker volume create portainer_dataCreate and run a Docker container from Portainer image.
docker run -d \
--name portainer-01 \
--restart unless-stopped \
-p 9000:9000 \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
-v portainer_data:/data \
portainer/portainerWe mounted the volume portainer_data in portainer1 container and published the service port 9000.
60Pcs Demon Movie Hunters Stickers, Korean Idol Sticker Anime Style Stickers for Water Bottles, Huntrx, Saja Boys, Jinwoo, Rumi, Tiger, Zoeystery, Miromabby Decal Gifts for Kids Men and Women (60)
10% OffConfigure Linux Firewall
By publishing the service port 9000, we have mapped it with the service port 9000 of Docker host. Therefore, we have to allow this service port in host’s firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=9000/tcp
firewall-cmd --reloadAccess Portainer Web UI
Browse URL https://docker-manager-01.example.com:9000/ and create Portainer’s initial admin account.
Note: If you do not create a Portainer admin account within 5 minutes after starting the portainer1 container. The container will be stopped automatically and then you have to start it again.
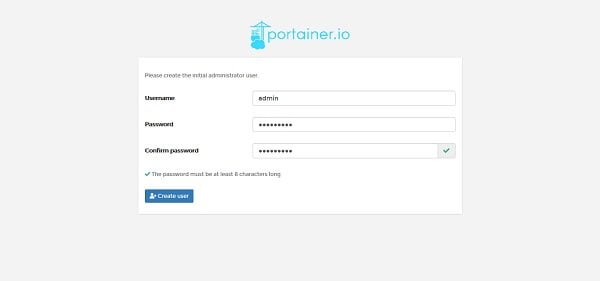
Enter a password and then click on Create User.
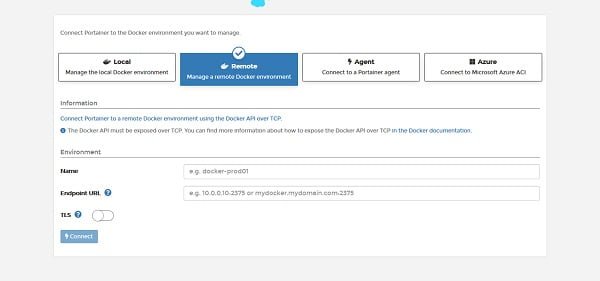
We are now at the connect with Docker environment page. Click on Local.
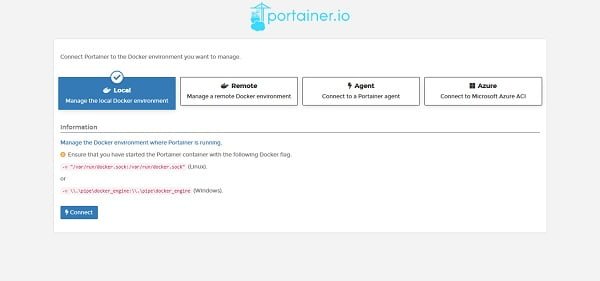
Click on Connect.
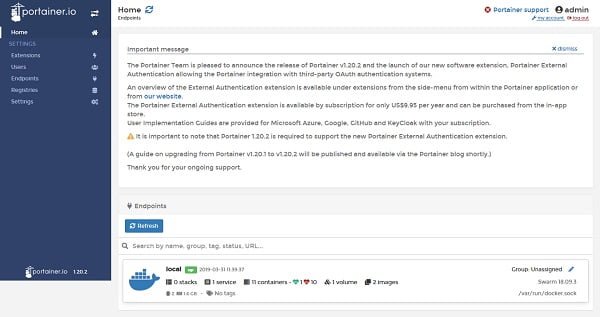
Click on the Local endpoint.
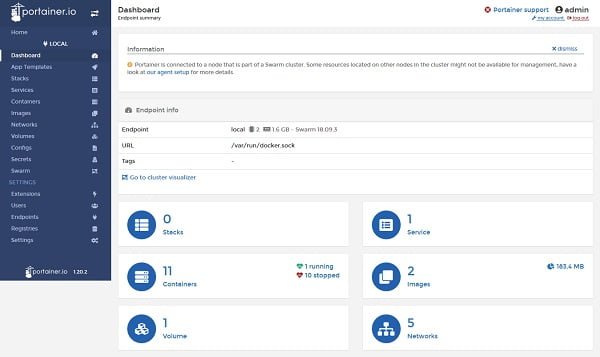
Click on the Swarm from left side panel.
Click on Containers from left side panel.
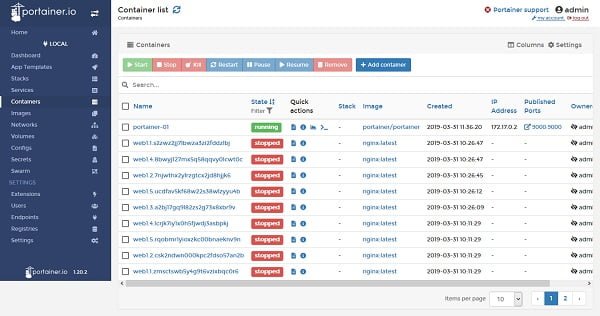
We can manage our complete Docker platform from Portainer Web UI including images, container, services, volumes, registries, clusters, stacks, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Portainer?
Portainer is a lightweight, user-friendly management UI for Docker and Kubernetes, making it easier to manage containers without using the command line.
Do I need Docker installed before setting up Portainer?
Yes, Portainer requires Docker to be installed and running on your CentOS 7 system before installation.
Can I access Portainer remotely?
Yes, after installation, you can access Portainer via a web browser using your server’s IP address and the assigned port (default: 9000).
Is Portainer free to use?
Yes, Portainer has a free community edition with essential features for container management.
How do I secure my Portainer installation?
Always set a strong admin password during setup, use HTTPS, and restrict access to trusted IPs for better security.
Amazon Fire TV Stick 4K Select (newest model), start streaming in 4K, AI-powered search, and free & live TV
$39.99 (as of October 27, 2025 18:39 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Final Thoughts
Installing Portainer on CentOS 7 provides a simple yet powerful way to manage your Docker environments through an intuitive web-based interface. With Portainer set up, you can easily deploy, monitor, and manage containers, networks, and volumes without the complexity of command-line operations.
To ensure a secure and efficient management experience, remember to secure your Portainer instance with proper authentication and SSL configuration. With this installation complete, you are now equipped to streamline your container management and improve operational efficiency on your CentOS 7 system.
Searching for a skilled Linux admin? From server management to security, I ensure seamless operations for your Linux systems. Find out more on my Freelancer profile!
Thank you for following along, and best of luck with your Portainer installation on CentOS 7!



Leave a Reply
Please log in to post a comment.