Unlock the power of container-native infrastructure—learn how to install Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host 7 today! Don’t fall behind in the DevOps race—discover the fast, secure, and scalable OS built for modern cloud deployments. Act now and future-proof your environment! #centlinux #linux #docker
Table of Contents
What is Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host?
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host 7 or Red Hat Atomic Host 7 (in short) is a variant of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7. It is a minimal operating system optimized for container hosting using Docker. Just like RHEL 7, Red Hat Atomic Host 7 is also open source. Atomic Host is the part of Project Atomic that is an upstream collection of open source container operating systems.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host (RHEL Atomic Host) is a minimalist, container-optimized version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux designed specifically for running containerized applications. Here are the key features and characteristics of RHEL Atomic Host:
- Lightweight and Minimalistic: Unlike the traditional RHEL, Atomic Host is stripped down to include only the essential components needed to run containers, reducing the overhead and attack surface.
- Atomic Upgrades: It supports atomic upgrades and rollbacks, meaning you can update the entire system image in a single operation and easily revert to the previous version if something goes wrong. This ensures that updates are reliable and can be performed without fear of breaking the system.
- Docker and Kubernetes: RHEL Atomic Host is optimized for Docker and Kubernetes, providing a robust and secure platform for building, deploying, and managing containerized applications. It comes with Docker pre-installed and is fully compatible with Kubernetes orchestration.
- Immutable Infrastructure: The operating system is designed to be immutable, meaning that it remains unchanged during runtime. This immutability improves security and reliability by ensuring that the system state is consistent and predictable.
- Security: Red Hat includes various security features and tools to ensure that the container host remains secure. This includes SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) policies tailored for containers, ensuring that containerized applications run in a confined and secure environment.
- Support and Integration: As part of the Red Hat ecosystem, Atomic Host benefits from Red Hat’s enterprise-grade support and integration with other Red Hat products and services, providing a seamless experience for users in enterprise environments.
Overall, RHEL Atomic Host is ideal for organizations looking to leverage container technologies for application deployment while maintaining a focus on security, efficiency, and ease of management.
Recommended Training: Docker Mastery: with Kubernetes +Swarm from a Docker Captain

Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host vs K3OS
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host (RHEL Atomic Host) and K3OS are both lightweight operating systems designed to optimize the running of containerized applications, but they differ in several key aspects. Here’s a comparison between the two:
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host (RHEL Atomic Host)
Purpose:
- Designed specifically for running containerized applications using Docker and Kubernetes.
- Targets enterprise environments with robust security and support.
Base OS:
- Based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux, providing a stable and secure foundation.
Atomic Upgrades:
- Supports atomic upgrades and rollbacks, allowing seamless updates and easy reversion to previous states.
Security:
- Includes SELinux policies tailored for containers, enhancing security.
- Benefit from Red Hat’s enterprise-grade security features and support.
Ecosystem Integration:
- Part of the larger Red Hat ecosystem, integrating well with other Red Hat products and services.
Deployment and Management:
- Designed to work with Docker and Kubernetes.
- Emphasizes ease of management in enterprise environments.
K3OS
Purpose:
- Specifically optimized for running K3s, a lightweight Kubernetes distribution designed for resource-constrained environments and edge computing.
Base OS:
- Built on top of Alpine Linux, known for its small footprint and simplicity.
Lightweight and Simple:
- Extremely lightweight, making it suitable for edge devices, IoT, and other environments with limited resources.
- Emphasizes simplicity and minimalism.
Deployment and Management:
- Seamlessly integrates with K3s, providing a streamlined Kubernetes experience.
- Designed for rapid deployment and ease of use in small clusters or edge environments.
Security:
- Uses minimal base components, reducing the attack surface.
- Leverages Kubernetes’ built-in security features and practices.
Ecosystem Integration:
- Tailored for use with K3s, but can integrate with other cloud-native tools and services.
- Community-driven with support from the broader Kubernetes ecosystem.
Key Differences
Target Use Case:
- RHEL Atomic Host is aimed at enterprise environments needing robust support and security features.
- K3OS is tailored for lightweight Kubernetes deployments, particularly in edge and resource-constrained environments.
Base Operating System:
- RHEL Atomic Host uses Red Hat Enterprise Linux, offering enterprise stability and support.
- K3OS is based on Alpine Linux, focusing on minimalism and low resource usage.
Integration with Kubernetes:
- RHEL Atomic Host integrates with full Kubernetes installations, suitable for larger, more complex environments.
- K3OS is optimized for K3s, a lightweight Kubernetes distribution, making it ideal for smaller clusters and edge use cases.
Management and Updates:
- RHEL Atomic Host offers atomic upgrades and rollbacks for reliable updates.
- K3OS focuses on simplicity and rapid deployment, with easy integration into K3s environments.
Conclusion
Both RHEL Atomic Host and K3OS provide specialized solutions for running containerized applications, but they cater to different needs and environments. RHEL Atomic Host is suitable for enterprises needing robust support, security, and integration with the Red Hat ecosystem, while K3OS excels in lightweight, edge, and resource-constrained scenarios with its streamlined approach and tight integration with K3s.
Virtual Machine Specification
In this article, we will install Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host 7.
Note: CentOS Atomic Host 7 is also available to download from CentOS website and it can be installed by using the same procedure as of Red Hat Atomic Host 7.
We have provisioned a virtual machine with following hardware specification:
- CPU – 2.4 Ghz (4 cores)
- Memory – 4 GB
- Storage – 40 GB
GKLSPL 65W USB C Laptop Charger Compatible with Dell Laptop Charger and More Chromebook Type C Power Cord
$8.99 (as of July 4, 2025 20:44 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Required Software for Atomic Host
We only required the Red Hat Atomic Host 7 ISO. Therefore, download it from Red Hat Customer Portal.
Install Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host 7
Insert / Attach Red Hat Atomic Host 7 ISO into the virtual machine’s CDROM and Power-On that virtual machine.
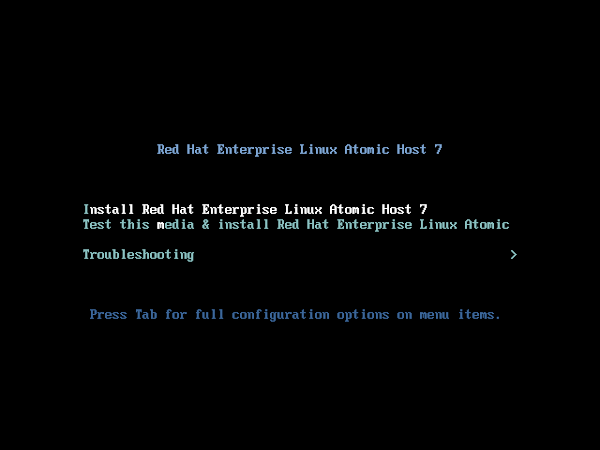
After boot, we are now at the boot menu of Linux.
Select option Install Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host 7 and press <ENTER>.
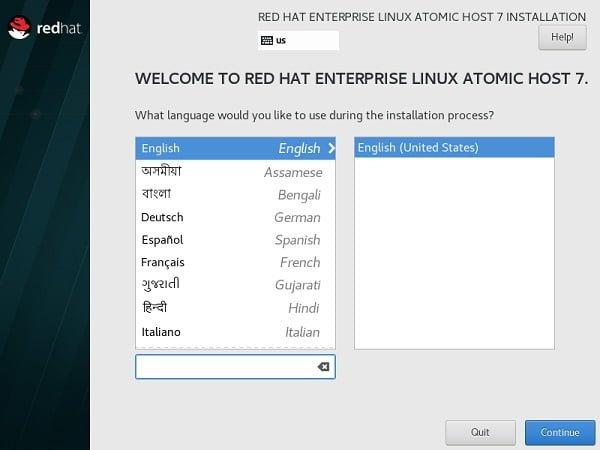
Select Language to be used during installation process of Red Hat Atomic Host 7.
Click on Continue.

We are now at the Installation Summary screen. It is the central point where we can perform all configurations.
First of all, we will set Date & Time of our Red Hat Atomic Host 7.
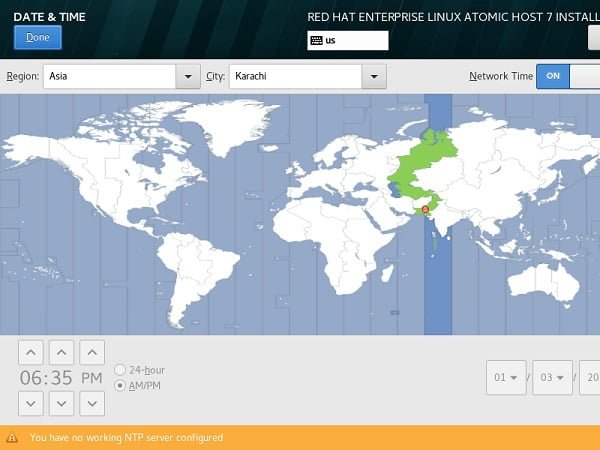
Set Time Zone and Date & Time here.
Click on Done.
We are again at Installation Summary screen. Click on Installation Destination to create disk partitions.
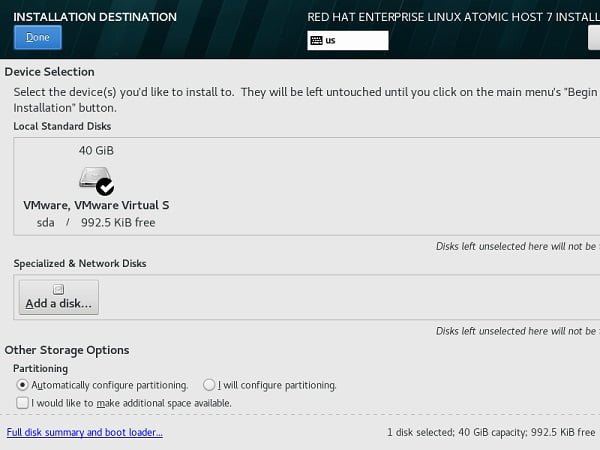
Linux installer automatically creates a partition layout from default template.
If you would like to create a custom layout, then create it here or click on Done to accept default layout.
We are again at Installation Summary screen. Click on Network and Hostname to perform network configurations.
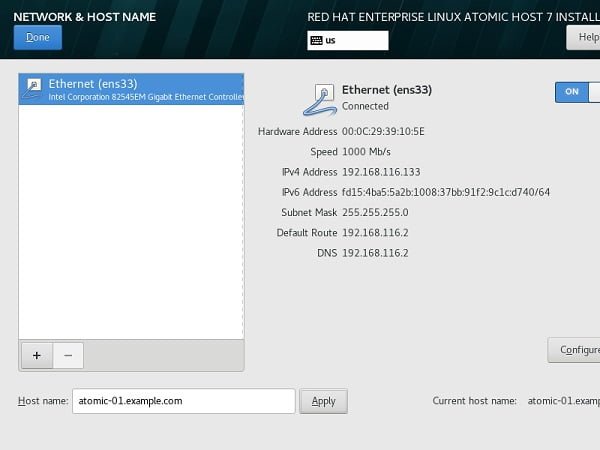
Set a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) and configure DHCP based-network.
Click on Done.
At Installation Summary screen, click on KDUMP.
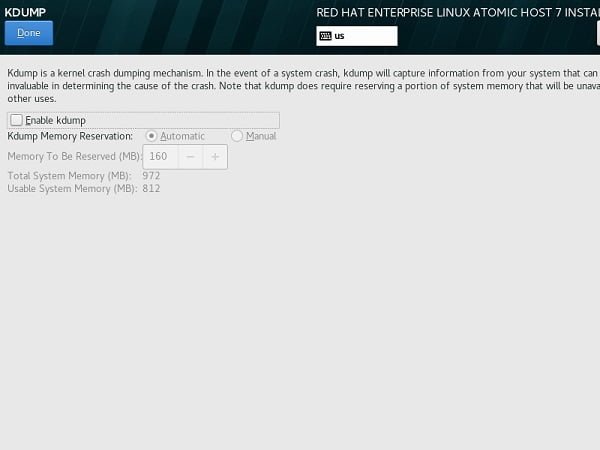
We are installing Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host 7 on a virtual machine with limited memory, therefore we have to disable the KDUMP.
Click on Done.
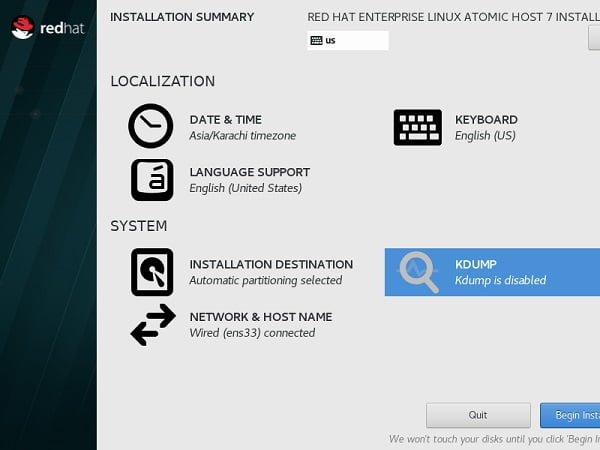
Click on Begin Installation.
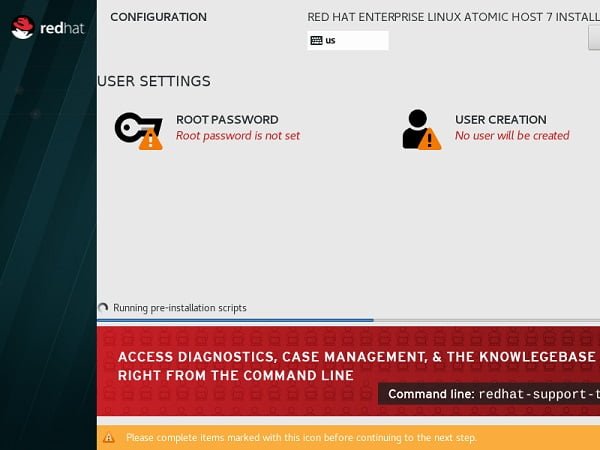
Set root user Password and Create another user ahmer as follows:
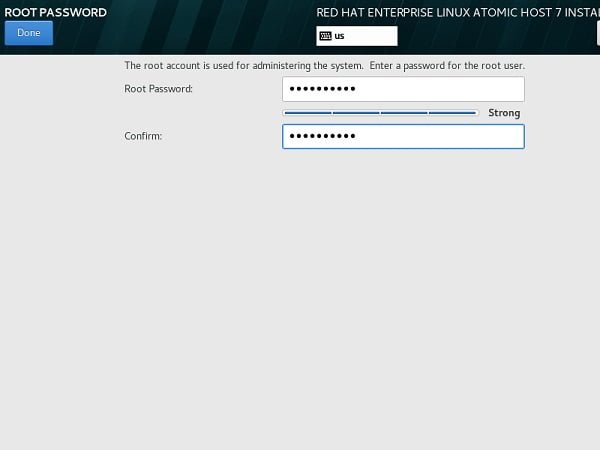
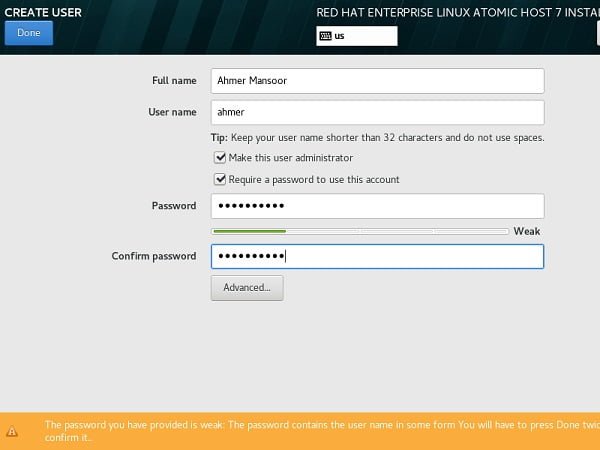
Click on Done.
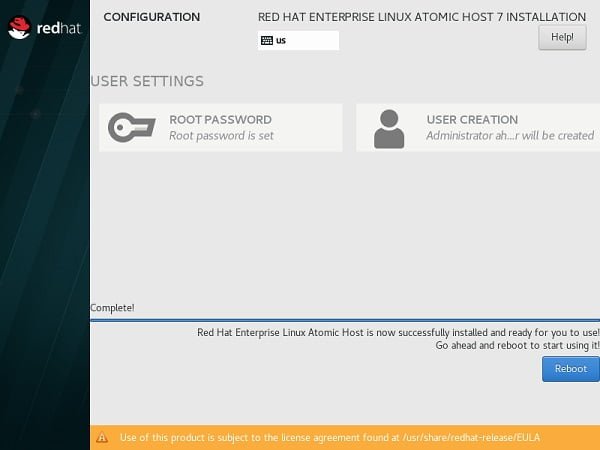
When Red Hat Atomic Host 7 installation completed, click on Reboot.
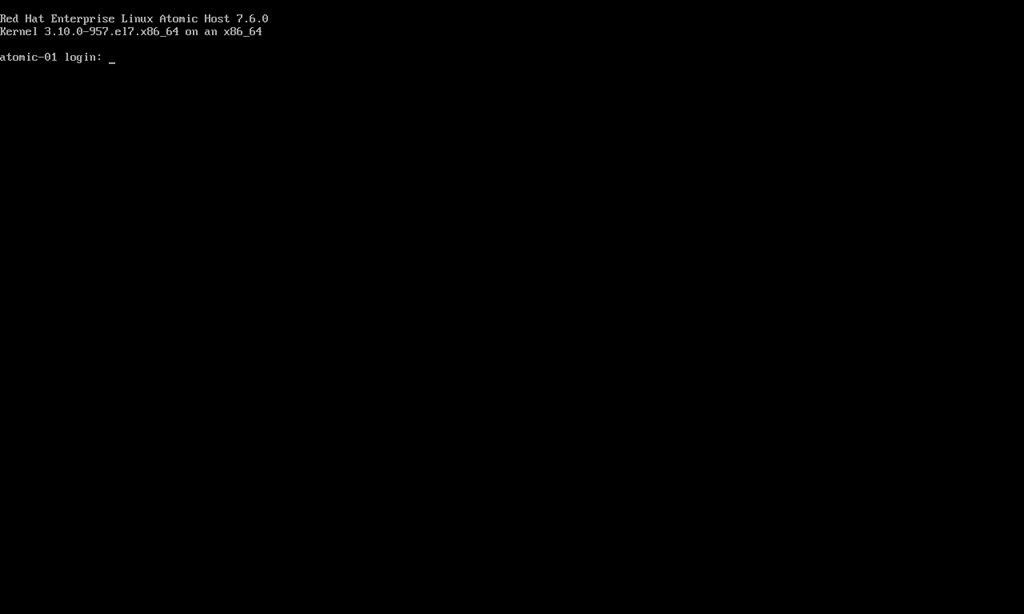

Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host 7 has been successfully installed.
LEARN MALTEGO: Master OSINT Investigations, Relationship Analysis, and Cyber Intelligence (KALI LINUX EXTREME USA Book 17)
$4.99 (as of July 4, 2025 20:44 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Final Thoughts
Installing Red Hat Enterprise Linux Atomic Host 7 sets the stage for a lightweight, container-optimized operating system designed for modern application deployment. By following the installation steps, you’ve deployed a secure, minimal OS tailored for running Docker containers at scale.
This setup enables faster provisioning, simplified updates with atomic transactions, and seamless integration into container-based workflows. To get the most out of Atomic Host, continue exploring Red Hat’s ecosystem tools and stay updated with best practices in container management and orchestration.
Struggling with Linux server management? I offer professional support to ensure your servers are secure, optimized, and always available. Visit my Fiverr profile to learn more!
Let’s get your system up and running efficiently!



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.