Learn how to setup Apache Reverse Proxy on CentOS 7. Follow our step-by-step guide to configure your server for enhanced performance and security. #centlinux #linux #apache
Table of Contents
What is Apache HTTP Server?
Apache HTTP Server, usually called as Apache, is the most popular web server over the Internet. Apache is free and open-source. Apache is developed and maintained by open-source community at Apache Software Foundation. Apache is loaded with so many features, and additional features can be added to Apache using the Apache modules.
Besides web server, Apache can also be configured as a Reverse Proxy to create a load balancing cluster of two or more web servers. This functionality can be added to Apache via mod_proxy module. Apache HTTP Server can be used to configure load balancers, hot-spares, hot-standby and failover nodes.

In this article, we will setup Apache reverse proxy and an HTTP load balancer on CentOS 7 server.
Read Also: How to setup Nginx Reverse Proxy in CentOS 7
System Specification
In this article, we are using three virtual machines. Two VMs to deploy and run two websites and One VM to configure as the reverse proxy and HTTP load balancer.
| Hostname | web-01.example.com | web-02.example.com | proxy-01.example.com |
| IP Address | 192.168.116.51/24 | 192.168.116.52/24 | 192.168.116.53/24 |
| Operating System | CentOS 7.6 | CentOS 7.6 | CentOS 7.6 |
We have already configured web-01.example.com and web-02.example.com as the web servers and hosted a simple and distinct webpage on both servers.


Now, we will configure the proxy-01.example.com as the load balancer using mod_proxy and Apache HTTP server.
Install Apache on CentOS 7
Connect to proxy-01.example.com as root user.
Install Apache HTTP Server using yum command.
yum install -y httpdStart and enable httpd.service.
systemctl start httpd.service
systemctl enable httpd.serviceAllow HTTP service in Linux firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
firewall-cmd --reloadBrowse URL http://proxy-01.example.com in a client browser.
Our Apache HTTP Server is running and displaying a default test page.
Setup Apache Reverse Proxy in CentOS 7
Apache HTTP Server requires mod_proxy module to configure and function as the Load Balancer. The mod_proxy module is contained in httpd package, therefore it is automatically installed alongwith Apache HTTP Server on CentOS 7 platforms.
Use the following command to verify the availability of mod_proxy.
httpd -M | grep proxyOutput:
proxy_module (shared)
proxy_ajp_module (shared)
proxy_balancer_module (shared)
proxy_connect_module (shared)
proxy_express_module (shared)
proxy_fcgi_module (shared)
proxy_fdpass_module (shared)
proxy_ftp_module (shared)
proxy_http_module (shared)
proxy_scgi_module (shared)
proxy_wstunnel_module (shared)
Add a configuration file in /etc/httpd/conf.d/.
vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/proxy.confAdd following reverse proxy configurations therein.
<proxy balancer://appset>
BalancerMember http://web-01.example.com
BalancerMember http://web-02.example.com
ProxySet lbmethod=bytraffic
</proxy>
ProxyPass "/app" "balancer://appset/"
ProxyPassReverse "/app" "balancer://appset/"Restart httpd.service.
systemctl restart httpd.serviceBrowse URL http://proxy-01.example.com/app in a client browser.

Our reverse proxy configuration has been working and the Page Request has been forwarded to web-01.example.com.
Refresh the Web Page.

This time our Page Request has been served by web-02.example.com.
We have configured a simple reverse proxy in Apache HTTP server, that is load balancing between two web servers.
mod_proxy has many configuration options and we can create relatively advanced configurations such as hot-spare, hot-standby and failover sets. Complete documentations is available at Apache Website. You can experiment on your own by reading documentation and enhancing the same configurations that we have created above.
Configure Balancer Manager
Apache HTTP Server also provide a built-in Balancer-Manager application for easy management and monitoring of load balancers.
Add following configuration file in /etc/httpd/conf.d.
vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/lbmanager.confAdd following directives to enable Balancer-Manager.
<location "/balancer-manager">
SetHandler balancer-manager
allow from all
</location>Restart httpd.service.
systemctl restart httpd.serviceBrowse URL http://proxy-01.example.com/balancer-manager from a client browser.
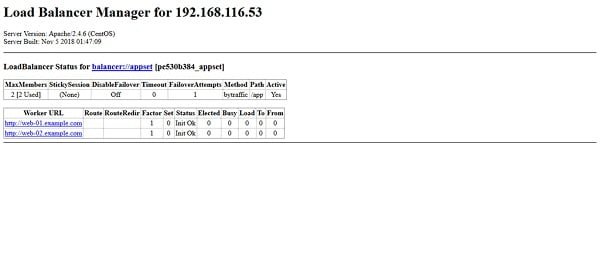
Balancer-Manager is configured and ready to use.
Securing Balancer Manager
Balancer Manager is a simple application for monitoring and management of Apache HTTP Load Balancer. Therefore, it also lacks any implicit user authentication. However, we can configure Basic HTTP Authentication to restrict unauthorized access.
Create a password file and add a user in it.
htpasswd -c /etc/httpd/htpasswd ahmerModify /etc/httpd/conf.d/lbmanager.conf to implement basic HTTP authentication.
vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/lbmanager.confThe updated configurations should be as follows:
<location "/balancer-manager">
SetHandler balancer-manager
AuthType "basic"
AuthName "balancer-manager"
AuthUserFile /etc/httpd/htpasswd
Require valid-user
</location>Restart httpd.service.
systemctl restart httpd.serviceBrowse URL http://proxy-01.example.com/balancer-manager from a client browser.
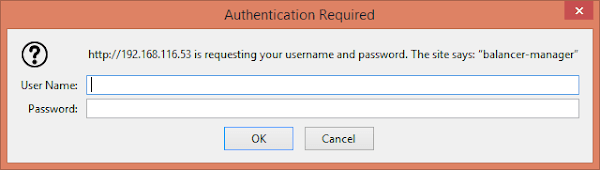
Now, it is asking for a valid user to login.
We have successfully setup Apache Reverse Proxy in CentOS 7. If you like this article, then you should read my article “HAProxy: Configure HTTP Load Balancer in CentOS 7”.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a reverse proxy?
A reverse proxy acts as an intermediary between clients and backend servers, forwarding requests and returning responses without exposing the internal servers directly.
Why use Apache as a reverse proxy?
Apache is lightweight, widely supported, and easy to configure, making it a good choice for load balancing, SSL termination, and hiding backend server details.
What prerequisites are needed?
You need a CentOS 7 server with Apache installed, sudo/root access, and backend servers (e.g., web apps) running on other ports or machines.
Does Apache support reverse proxy by default?
Yes, but you need to enable the required modules (mod_proxy and mod_proxy_http) and configure them properly in the Apache settings.
How do I test if the reverse proxy is working?
After configuration, access your Apache server’s domain or IP in a browser. If it correctly displays content from your backend server, the proxy is working.
Final Thoughts
Setting up an Apache reverse proxy on CentOS 7 provides a powerful way to route client requests to backend servers while leveraging Apache’s stability and extensive module support. By enabling the necessary proxy modules, configuring virtual hosts, and adjusting firewall and SELinux settings, you’ve created a secure and efficient reverse proxy environment.
This setup enhances scalability, simplifies backend management, and allows for features like load balancing and SSL offloading. Regular maintenance and monitoring will ensure continued performance and reliability.
Whether you need cloud optimization, server management, or automation, I provide comprehensive AWS and Linux services. Hire me to elevate your systems.
Recommended Courses
If you’re serious about mastering web hosting and server management, the Apache Web Server by Vipin Gupta online course is a perfect choice. This beginner-friendly yet comprehensive training will guide you through Apache installation, configuration, optimization, and troubleshooting—all the essential skills you need to confidently manage real-world server environments.
Whether you’re a student, system administrator, or developer, this course will give you practical knowledge that you can immediately apply in your projects or career. Enroll now through my affiliate link and start building your expertise in one of the world’s most popular web servers.
Disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links. If you purchase through these links, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.