Learn how to install OpenLDAP on CentOS 7 with our comprehensive step-by-step guide. Set up and manage your directory services efficiently with LDAP Server. #centlinux #linux #cybersecurity
Table of Contents
What is OpenLDAP?
OpenLDAP is a free and open-source implementation of the Light Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). The LDAP is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an IP network. Directory services play an important role in developing intranet and Internet applications by allowing the sharing of information about users, systems, networks, services, and applications throughout the network.
OpenLDAP is an open-source implementation of the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). It provides directory services, which are essential for organizing and managing information in a network, such as user data, access control information, and configuration settings. Here are some key aspects:
- Directory Service: It acts as a directory service that stores and retrieves data in a hierarchical and organized manner. This is particularly useful for managing user credentials, group memberships, and other network resources.
- LDAP Protocol: LDAP is a protocol used to access and maintain distributed directory information services over a network. OpenLDAP implements this protocol, allowing it to interact with other LDAP-compatible applications and services.
- Scalability and Flexibility: OpenLDAP is highly scalable, making it suitable for both small and large deployments. It can handle a large number of entries and provides various configuration options to suit different use cases.
- Security Features: OpenLDAP supports various security mechanisms, including SSL/TLS encryption, SASL authentication, and access control lists (ACLs) to protect directory data and ensure secure access.
- Replication and High Availability: OpenLDAP supports replication, allowing directory data to be copied across multiple servers for redundancy and high availability. This ensures that the directory service remains available even if one server fails.
- Extensibility: OpenLDAP is extensible through overlays and modules, which add additional functionality and customization options. This makes it adaptable to a wide range of requirements.
- Administration Tools: OpenLDAP includes various tools for administration and management, such as command-line utilities and graphical interfaces like phpLDAPadmin, which simplify directory management tasks.
- Community and Support: Being an open-source project, OpenLDAP has a large and active community that contributes to its development and provides support through forums, mailing lists, and documentation.
Overall, OpenLDAP is a powerful and flexible directory service solution widely used in various environments to manage directory information efficiently and securely.
Recommended Online Training: Learn Bash Shell in Linux for Beginners

Read Also: How to install phpLDAPadmin on CentOS 7
Linux Server Specification
In this post, I will demonstrate you how to configure a Central Remote Authentication Server using OpenLDAP v2.4 on platform CentOS / RHEL 7.
For this demonstration, I have provisioned a VM with following specification. Please do not confuse these specification with the minimum system requirements for OpenLDAP.
- CPU – 2.4 Ghz (1 core)
- Memory – 1 GB
- Storage – 20 GB
- Swap – 2 GB
- Operating System – CentOS 7.0
I have done some initial configurations in VM, that includes setting up hostname, IP address and Yum Repository.
- Hostname – ldapserver.itlab.com
- IP Address – 192.168.116.3/24
Install OpenLDAP on CentOS 7
Login to VM with root user, and install openldap packages.
# yum -y install openldap compat-openldap openldap-clients openldap-servers openldap-devel
Create database from template.
# cp /usr/share/openldap-servers/DB_CONFIG.example /var/lib/ldap/DB_CONFIG # slaptest -u config file testing succeeded # chown ldap:ldap /var/lib/ldap/*
Start and Enable the slapd service.
# systemctl enable slapd && systemctl start slapd ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/slapd.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/slapd.service'
Allow ldaps port in Firewall.
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ldaps success # firewall-cmd --reload success
Configure OpenLDAP syslog.
# cat >> /etc/rsyslog.conf << EOF > #LDAP Logging > local4.* /var/log/openldap.log > EOF # systemctl restart rsyslog
Add required schemas to our OpenLDAP Directory.
# ldapadd -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -D "cn=config" -f /etc/openldap/schema/cosine.ldif SASL/EXTERNAL authentication started SASL username: gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth SASL SSF: 0 adding new entry "cn=cosine,cn=schema,cn=config" # ldapadd -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -D "cn=config" -f /etc/openldap/schema/nis.ldif SASL/EXTERNAL authentication started SASL username: gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth SASL SSF: 0 adding new entry "cn=nis,cn=schema,cn=config"
Generate Password hash 123 for Directory Manager.
# slappasswd
New password:
Re-enter new password:
{SSHA}mNOljCtwWbG0P88Hu+jqsrkUOzjfqvakCopy the Password hash, we will need it in later configurations. Add initial database configurations.
# mkdir ~/ldap # cd ~/ldap
# cat > db.ldif << EOF > dn: olcDatabase={2}hdb,cn=config > changetype: modify > replace: olcSuffix > olcSuffix: dc=itlab,dc=com > > dn: olcDatabase={2}hdb,cn=config > changetype: modify > replace: olcRootDN > olcRootDN: cn=ldapadm,dc=itlab,dc=com > > dn: olcDatabase={2}hdb,cn=config > changetype: modify > replace: olcRootPW > olcRootPW: {SSHA}mNOljCtwWbG0P88Hu+jqsrkUOzjfqvak > EOF # ldapmodify -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f db.ldif SASL/EXTERNAL authentication started SASL username: gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth SASL SSF: 0 modifying entry "olcDatabase={2}hdb,cn=config" modifying entry "olcDatabase={2}hdb,cn=config" modifying entry "olcDatabase={2}hdb,cn=config"
Since, we are planning to run this service in TLS mode, therefore, must required to create security certificates for this purpose. For simplicity, I am using Self-Signed certificates, However, you can use a Signed Certificate, if you have a Certification Authority (CA) configured for your network.
# openssl req -new -x509 -nodes -out /etc/openldap/certs/ldapserver.pem -keyout /etc/openldap/certs/ldapserver.key -days 365 Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key .........................+++ ..................................................................+++ writing new private key to '/etc/openldap/certs/ldapserver.key' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:PK State or Province Name (full name) []:Sindh Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Karachi Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:XYZ Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:IT Lab Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:ldapserver.itlab.com Email Address []:root@ldapserver.itlab.com # cd /etc/openldap/certs # chown ldap:ldap * # chmod 600 ldapserver.key
Edit the following directive in /etc/sysconfig/slapd to enable service to run in TLS mode.
SLAPD_URLS="ldapi:/// ldap:/// ldaps:///"
Now, add security certificate and private key to LDAP configurations.
# cd ~/ldap # cat > cert.ldif << EOF > dn: cn=config > changetype: modify > replace: olcTLSCertificateFile > olcTLSCertificateFile: /etc/openldap/certs/ldapserver.pem > > dn: cn=config > changetype: modify > replace: olcTLSCertificateKeyFile > olcTLSCertificateKeyFile: /etc/openldap/certs/ldapserver.key > > dn: cn=config > changetype: modify > replace: olcLogLevel > olcLogLevel: -1 > EOF # ldapmodify -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f cert.ldif SASL/EXTERNAL authentication started SASL username: gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth SASL SSF: 0 modifying entry "cn=config" modifying entry "cn=config" modifying entry "cn=config"
Create directory, LDAP Manager user, and two Organisational units for holding users and groups entries.
# cd ~/ldap # cat > base.ldif << EOF > dn: dc=itlab,dc=com > dc: itlab > objectClass: top > objectClass: domain > > dn: cn=ldapadm ,dc=itlab,dc=com > objectClass: organizationalRole > cn: ldapadm > description: LDAP Manager > > dn: ou=People,dc=itlab,dc=com > objectClass: organizationalUnit > ou: People > > dn: ou=Groups,dc=itlab,dc=com > objectClass: organizationalUnit > ou: Groups > EOF # ldapadd -x -W -D "cn=ldapadm,dc=itlab,dc=com" -f base.ldif Enter LDAP Password: adding new entry "dc=itlab,dc=com" adding new entry "cn=ldapadm ,dc=itlab,dc=com" adding new entry "ou=People,dc=itlab,dc=com" adding new entry "ou=Groups,dc=itlab,dc=com"
Define access levels for the directory.
# cd ~/ldap
# cat > access.ldif << EOF
> dn: olcDatabase={1}monitor,cn=config
> changetype: modify
> replace: olcAccess
> olcAccess: {0}to * by dn.base="gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external, cn=auth" read by dn.base="cn=ldapadm,dc=itlab,dc=com" read by * none
>
> changetype: modify
> replace: olcAccess
> olcAccess: {0}to dn.subtree="dc=itlab,dc=com" by dn.base="cn=ldapadm,dc=itlab,dc=com" manage by * read
> EOF
# ldapmodify -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f access.ldif
SASL/EXTERNAL authentication started
SASL username: gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth
SASL SSF: 0
modifying entry "olcDatabase={1}monitor,cn=config"Let’s create three groups. Groups ahmer & mansoor here are defined to be utilized as the Primary groups for the Users ahmer & mansoor. While group dba will be used as a suplementary group for both users.
# cd ~/ldap # cat > groups.ldif << EOF > dn: cn=ahmer,ou=Groups,dc=itlab,dc=com > cn: ahmer > objectClass: posixGroup > objectClass: top > gidNumber: 10001 > memberuid: ahmer > > dn: cn=mansoor,ou=Groups,dc=itlab,dc=com > cn: mansoor > objectClass: posixGroup > objectClass: top > gidNumber: 10002 > memberuid: mansoor > > dn: cn=dba,ou=Groups,dc=itlab,dc=com > cn: dba > objectClass: posixGroup > objectClass: top > gidNumber: 10003 > memberuid: ahmer > memberuid: mansoor > EOF # ldapadd -x -W -D "cn=ldapadm,dc=itlab,dc=com" -f groups.ldif Enter LDAP Password: adding new entry "cn=ahmer,ou=Groups,dc=itlab,dc=com" adding new entry "cn=mansoor,ou=Groups,dc=itlab,dc=com" adding new entry "cn=dba,ou=Groups,dc=itlab,dc=com"
Now create users.
# cd ~/ldap
# cat > users.ldif << EOF
> dn: uid=ahmer,ou=People,dc=itlab,dc=com
> uid: ahmer
> cn: ahmer
> objectClass: account
> objectClass: posixAccount
> objectClass: top
> objectClass: shadowAccount
> userPassword: {crypt}a
> shadowLastChange: 17665
> shadowMin: 0
> shadowMax: 99999
> shadowWarning: 7
> loginShell: /bin/bash
> uidNumber: 10001
> gidNumber: 10001
> homeDirectory: /home/ahmer
>
> dn: uid=mansoor,ou=People,dc=itlab,dc=com
> uid: mansoor
> cn: mansoor
> objectClass: account
> objectClass: posixAccount
> objectClass: top
> objectClass: shadowAccount
> userPassword: {crypt}a
> shadowLastChange: 17665
> shadowMin: 0
> shadowMax: 99999
> shadowWarning: 7
> loginShell: /bin/bash
> uidNumber: 10002
> gidNumber: 10002
> homeDirectory: /home/mansoor
> EOF
# ldapadd -x -W -D "cn=ldapadm,dc=itlab,dc=com" -f users.ldif
Enter LDAP Password:
adding new entry "uid=ahmer,ou=People,dc=itlab,dc=com"
adding new entry "uid=mansoor,ou=People,dc=itlab,dc=com"Set passwords for the users.
# ldappasswd -S -x -D "cn=ldapadm,dc=itlab,dc=com" -W "uid=ahmer,ou=People,dc=itlab,dc=com" New password: Re-enter new password: Enter LDAP Password: # ldappasswd -S -x -D "cn=ldapadm,dc=itlab,dc=com" -W "uid=mansoor,ou=People,dc=itlab,dc=com" New password: Re-enter new password: Enter LDAP Password:
We can also use an LDAP browser utility to manage our directory. Following is a screenshot of our directory at this time.
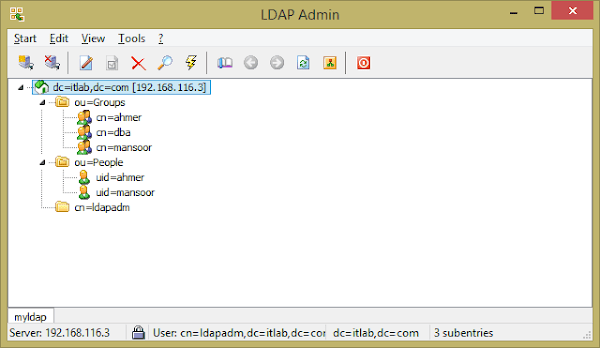
There are various commercial and free LDAP Directory Browsers and Admins tools are available. I used LDAPAdmin for this job.
Configure LDAP Client on CentOS 7
Now, I am going to configure a Linux client to use our LDAP directory for Remote Authentication. I have a client machine here with hostname=Desktop1, that I use for this purpose. First of all, make sure that hostname of our LDAP Directory Server must be resolvable, because we are using Hostname ldapserver.itlab.com for the Common Name in the Security Certificate.
# echo 192.168.116.3 ldapserver.itlab.com ldapserver >> /etc/hosts
Now install required packages.
# yum -y install openldap sssd Loaded plugins: langpacks, product-id, subscription-manager This system is not registered to Red Hat Subscription Management. You can use subscription-manager to register. Repodata is over 2 weeks old. Install yum-cron? Or run: yum makecache fast localyum | 4.1 kB 00:00:00 Package openldap-2.4.39-3.el7.x86_64 already installed and latest version Package sssd-1.11.2-65.el7.x86_64 already installed and latest version Nothing to do # systemctl start sssd && systemctl enable sssd ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/sssd.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/sssd.service'
Since, we are using LDAPS, therefore, we have to copy the Self-Signed Certificate to our client machine.
# scp root@ldapserver.itlab.com:/etc/openldap/certs/ldapserver.pem /etc/openldap/cacerts/ldapserver.pem The authenticity of host 'ldapserver.itlab.com (192.168.116.3)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is 4c:7f:83:39:d1:bc:ef:4c:fd:58:82:7b:36:ff:9e:f2. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added 'ldapserver.itlab.com,192.168.116.3' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. root@ldapserver.itlab.com's password: ldapserver.pem 100% 1452 1.4KB/s 00:00
Now configure Remote Authentication with LDAP on client machine.
# authconfig --update --enableldap --enableldapauth --enableldaptls --ldapserver=ldaps://ldapserver.itlab.com --ldapbasedn="dc=itlab,dc=com" --enablemkhomedir
Now connect using an LDAP User.
# su - ahmer
Creating directory '/home/ahmer'. Last login: Mon May 28 11:28:17 PDT 2018 on pts/0 $ id uid=10001(ahmer) gid=10001(ahmer) groups=10001(ahmer),10003(dba) context=unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023
Our client machine is now configured to authenticate to the LDAP remote authentication server.
If you are new to Linux and facing difficulty in working at Linux Bash prompt. We recommend that, you should read The Linux Command Line, 2nd Edition: A Complete Introduction by William Shotts.
Final Thoughts
Installing OpenLDAP on CentOS 7 can significantly enhance your network’s directory management capabilities, providing a robust and scalable solution for handling user data and access controls. Whether you’re setting up LDAP Server for the first time or looking to optimize your current configuration, this guide provides the essential steps to get you started.
If you need further assistance or prefer professional help with your LDAP Server installation and configuration, feel free to check out my Fiverr gig. I offer comprehensive services to ensure your LDAP setup is efficient and secure. Let me help you streamline your directory management with ease!

Dear sir i setup server and client in same machine. while using su – user1 its saying "user user1 does not exist" error message is coming . Please help me to solve it
Please check your LDAP client configurations. If problem persists than contact me at our Facebook page.
There's error during start up sssd service, so I have to setup sssd.conf by Googling another tutorials. Unfortunately, when using ldapsearch, I could get users & groups, but when I use id…, it saying "no such user".
Hello, is there lacking off a setup for sssd service?
Please contact me on our Facebook page.
Please contact me on our Facebook page.