Learn how to install Elastic Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana, and Beats) on CentOS 8 with our comprehensive guide. Set up powerful search, logging, and data visualization tools easily and efficiently. #centlinux #linux #elasticsearch #kibana #logstash
Table of Contents
What is Elastic Stack?
Elastic Stack, formerly known as ELK Stack, is a collection of open-source tools designed for search, logging, monitoring, and data analytics. It consists of Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana, and Beats, each playing a specific role in data ingestion, processing, storage, and visualization. Elasticsearch is the core component, acting as a powerful search and analytics engine. Logstash processes and transforms incoming data, Kibana provides real-time visualizations and dashboards, and Beats efficiently collects and ships data from various sources.
Elastic Stack is widely used for log management, security analytics, and observability in IT infrastructures. It helps organizations monitor systems, detect anomalies, and gain insights from structured and unstructured data. The stack is highly scalable and integrates with various cloud and on-premises environments, making it a popular choice for DevOps, security teams, and enterprise IT operations.

The Elastic Stack consists of four core components:
Elasticsearch
- Elasticsearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine built on Apache Lucene. It provides scalable and real-time search capabilities, allowing users to store, search, and analyze large volumes of data quickly and efficiently.
Kibana
- Kibana is a powerful data visualization and exploration tool that works seamlessly with Elasticsearch. It enables users to create interactive dashboards, charts, and graphs to visualize data stored in Elasticsearch indices. Kibana also provides features for ad-hoc analysis, data exploration, and real-time monitoring.
Beats
- Beats are lightweight data shippers that collect and send various types of data to Elasticsearch or Logstash for further processing. Beats are designed to be easy to deploy and use minimal system resources. There are different types of Beats for collecting different types of data, such as Filebeat for log files, Metricbeat for system metrics, Packetbeat for network traffic, and Auditbeat for audit data.
Logstash
- Logstash is a data processing pipeline that ingests, transforms, and enriches data before sending it to Elasticsearch or other destinations. It supports a wide range of input sources, including logs, metrics, events, and other data formats. Logstash can parse, filter, and manipulate data using a rich set of plugins, allowing users to preprocess data before indexing it into Elasticsearch.
Together, these components form a comprehensive data platform that enables organizations to collect, store, search, analyze, and visualize data in real-time. The Elastic Stack is widely used for various use cases, including log and event data analysis, monitoring and observability, security analytics, business intelligence, and more. Its flexibility, scalability, and extensibility make it a popular choice for organizations of all sizes looking to derive insights from their data.
Environment Specification
We are using a minimal CentOS 8 virtual machine with following specifications.
- CPU – 3.4 Ghz (4 cores)
- Memory – 4 GB
- Storage – 40 GB
- Operating System – CentOS Linux 8.3
- Hostname – elastic-stack.centlinux.com
- IP Address – 192.168.116.230 /24
For an optimal learning and testing experience when installing the Elastic Stack on CentOS 8, it’s highly recommended to use a dedicated environment such as a Mini PC or a reliable VPS hosting service like Bluehost. A Mini PC offers a compact, energy-efficient way to run your Linux server locally, giving you full control and hands-on practice.
[Grab a Mini PC for your Home Lab – Shop with Us!]
Alternatively, a Bluehost VPS provides scalable resources and easy remote access, making it perfect for experimenting with server configurations and Elastic Stack components without investing in physical hardware.
[Launch Your VPS Server with Bluehost – Reliable & Affordable!]
Using either option ensures a stable setup that closely mimics production environments, which helps you troubleshoot and optimize effectively.
Disclaimer: Please note that some of the links to Mini PCs and VPS providers are affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you, supporting the ongoing creation of helpful tech guides.
Read Also: How to install ELK Stack on CentOS 7
Update your Linux Server
Use a ssh client to connect with elastic-stack.centlinux.com server as root user.
It is a best practice to update existing software packages in your Linux operating system before installing any new software thereon.
Therefore, if your Linux server is not updated yet then you can execute the following command to update it.
dnf update -yAfter updating software packages, verify the Linux operating system and Kernel version.
cat /etc/redhat-release
uname -rOutput:
CentOS Linux release 8.3.2011
4.18.0-240.1.1.el8_3.x86_64
Install Java on CentOS 8
Elasticsearch software is written in Java, therefore it requires Java runtime environment for execution.
You can either install Java on CentOS 8 or use the open source alternative OpenJDK on your Linux server.
dnf install -y java-11-openjdkAfter installation check the version of Java.
java -versionOutput:
openjdk version "11.0.9" 2020-10-20 LTS
OpenJDK Runtime Environment 18.9 (build 11.0.9+11-LTS)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM 18.9 (build 11.0.9+11-LTS, mixed mode, sharing)
Install Elastic Stack Yum Repository
All Elastic Stack software are provided through a common Elastic yum repository. If you add this yum repository in your Linux server then, you can install Elastic Stack very easily.
Import the GPG key of the Elastic yum repository using rpm command.
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearchCreate a yum repository file in /etc/yum.repos.d directory.
vi /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repoAnd add following directives therein.
[elasticsearch]
name=Elasticsearch repository for 7.x packages
baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/yum
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
autorefresh=1
type=rpm-mdYou can use the baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/oss-7.x/yum if you wish to install only open source components of Elastic Stack.
Build yum cache for Elastic repository.
dnf makecacheOutput:
CentOS Linux 8 - AppStream 1.1 kB/s | 4.3 kB 00:03
CentOS Linux 8 - BaseOS 1.6 kB/s | 3.9 kB 00:02
CentOS Linux 8 - Extras 541 B/s | 1.5 kB 00:02
Elasticsearch repository for 7.x packages 262 kB/s | 19 MB 01:12
Metadata cache created.
Elastic yum repository has been installed successfully.
Install Elasticsearch on CentOS 8
Since, you have setup the Elastic yum repository. Therefore, you can install the latest stable release of Elasticsearch by using the dnf command.
dnf install -y elasticsearchAt the time of this writing, the Elasticsearch 7.10.1 is available. You must ensure that you have installed the same versions of the other Elastic Stack members for better compatibility.
If you are installing on a non-production server with limited memory, then you should reduced the Java memory pool size to run Elasticsearch in a limited memory server. Edit the jvm.options file in vim text editor.
vi /etc/elasticsearch/jvm.optionsFind the following settings in this file.
-Xms1g
-Xmx1gAnd update with the following values.
-Xms256m
-Xmx512mEnable and start Elasticsearch service.
systemctl enable --now elasticsearch.serviceTo verify that the Elasticsearch is configured successfully, you can execute the following command.
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/?pretty"Output:
{
"name" : "elastic-stack.centlinux.com",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "KdBYBVSVT8aZ7DqJCrQayQ",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.10.1",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "rpm",
"build_hash" : "1c34507e66d7db1211f66f3513706fdf548736aa",
"build_date" : "2020-12-05T01:00:33.671820Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.7.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}Elasticsearch has been installed and configured successfully.
Install Kibana on CentOS 8
Just like Elasticsearch, you can also install Kibana software from the same Elastic yum repository. You can use the dnf command as follows.
dnf install -y kibanaAfter successful installation of Kibana software, you are required to configure it for use.
Kibana uses a YAML file for configuration, located at /etc/kibana/kibana.yml. You can either find and update the required settings or execute the following script to configure Kibana settings in one go.
cat >> /etc/kibana/kibana.yml << EOF
server.port: 5601
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
server.name: "elastic-stack.centlinux.com"
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]
EOFCreate a Linux user to own Kibana software files and processes.
useradd kibanaChange ownership of the following directory.
chown -R kibana:kibana /usr/share/kibana/*
chown -R kibana:kibana /var/lib/kibana/Enable and start Kibana service.
systemctl enable --now kibana.serviceKibana service listens on default port 5601/tcp.
To make Kibana service usable for the network computers, you have to allow incoming traffic to this port in Linux firewall.
Execute the following commands to allow Kibana service port in Linux firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5601/tcp
firewall-cmd --reloadOpen URL http://elastic-stack.centlinux.com:5601 in a web browser.
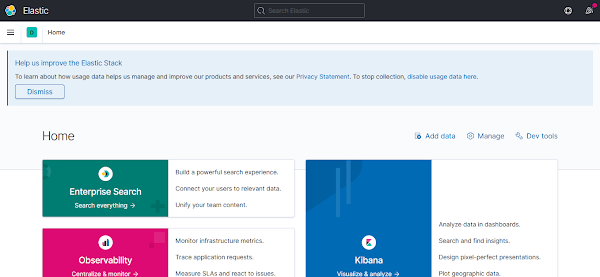
If you see the above web page then your Kibana software has been installed and configured successfully.
Install Logstash on CentOS 8
Logstash is also available in Elastic yum repository and you can execute dnf command to install it on your Linux server.
dnf install -y logstashLogstash can be run with default configurations, you are only required to enable and start the service by using systemctl command.
systemctl enable --now logstash.serviceInstall Beats on CentOS 8
For the sake of demonstration, we are only installing Filebeat on our Elastic Stack server. However, you can install any other member of Beats family by using same procedure.
Beats are also available in Elastic yum repository. Therefore use dnf command and install it on your Linux servers that you want to monitor via Elastic Stack.
dnf install -y filebeatAdd the system module to examine the local system logs.
filebeat modules enable systemRun the filebeat setup. It will scan your local system and connect itself with Kibana dashboard.
filebeat setupOutput:
Overwriting ILM policy is disabled. Set `setup.ilm.overwrite: true` for enabling.
Index setup finished.
Loading dashboards (Kibana must be running and reachable)
Loaded dashboards
Setting up ML using setup --machine-learning is going to be removed in 8.0.0. Please use the ML app instead.
See more: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/machine-learning/current/index.html
Loaded machine learning job configurations
Loaded Ingest pipelines
Enable and start Filebeat service.
systemctl enable --now filebeat.serviceClick on the Logs link under Elastic Observatory menu.
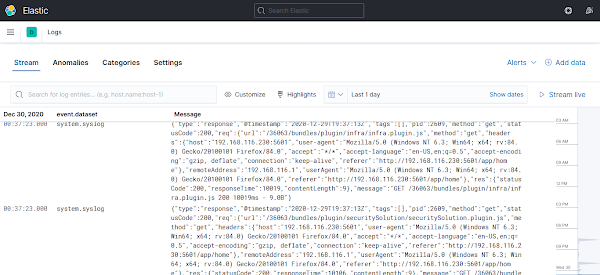
Install APM Server on CentOS 8
APM (Application Performance Monitoring) Server is the new entrant in Elastic Stack.
APM Server is an optional component, but it is recommended that you should install it alongwith Elastic Stack to monitor performance of your application servers and identify the bottlenecks therein.
Since, we already have all the system logs collected in our Elasticsearch database, therefore, installing APM server adds a analytical frontend in Elastic Observatory to pinpoint the actual cause of performance bottlenecks.
APM server is also available in Elastic yum repository. Therefore, install it by using dnf command.
dnf install -y apm-serverEnable and start APM Service.
systemctl enable --now apm-server.serviceFinal Thoughts
Mastering the installation of Elastic Stack on CentOS 8 opens a world of real-time data exploration, visualization, and analysis. With our guide, you’ll effortlessly set up Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana, and Beats, transforming your data into actionable insights.
Optimize your cloud infrastructure and secure your servers with my AWS and Linux administration services. Let’s ensure your systems run smoothly. Connect with me now! if you need any guidance or advice related to your Linux VPS.
FAQs
Q1: Can I install Elastic Stack on CentOS 8 minimal version without a GUI?
A1: Yes, Elastic Stack can be installed on CentOS 8 minimal without a GUI using the command line and systemd to manage services.
Q2: How do I check if Elasticsearch is running correctly after installation?
A2: Use following command to verify Elasticsearch returns cluster information.
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/"Q3: Is it necessary to configure firewall for Elastic Stack on CentOS 8?
A3: Yes, open ports 9200 for Elasticsearch and 5601 for Kibana in the firewall for external access.
Q4: Can I run multiple versions of Elastic Stack on the same CentOS 8 server?
A4: It’s not recommended due to port conflicts and resource usage; use containers or virtual machines instead.
Q5: How do I secure Elastic Stack on CentOS 8 after installation?
A5: Enable SSL/TLS, set up user authentication via X-Pack, and configure firewall rules for security.
Recommended Courses
If you’re looking to truly master Elasticsearch, the Complete Guide to Elasticsearch by Bo Andersen is one of the most comprehensive online courses available. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, this course walks you through everything from the basics to advanced concepts, with practical examples that make complex topics easier to understand.
It’s a perfect resource for anyone aiming to boost their search and analytics skills while staying competitive in today’s data-driven world. Enroll in the course here and start building expertise that will set you apart.
Disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links. If you purchase through these links, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

One response to “How to install Elastic Stack on CentOS 8”
thanks for the guide – for oss options be sure to append -oss to the dnf install commands