Learn how to install Cacti Server on CentOS 8 with this comprehensive guide. Follow step-by-step instructions to set up and configure Cacti for efficient network monitoring and performance tracking. #centlinux #linux #cacti
Table of Contents
What is Cacti Server?
Cacti is an open-source network monitoring and graphing tool designed to provide a robust solution for monitoring and visualizing the performance of network devices and servers. It is particularly useful for tracking metrics over time and identifying trends or issues in network performance. Here are some key features and aspects of Cacti:
Key Features of Cacti
Data Collection:
- Cacti can collect data from a variety of sources using SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), scripts, and other methods.
- It supports both built-in and custom data collection scripts, allowing for flexibility in monitoring different types of devices and metrics.
Graphing:
- Cacti excels in creating detailed and customizable graphs to visualize collected data.
- Users can create graphs with multiple data sources and customize the appearance and format to meet specific needs.
Templates:
- Cacti includes templates for graphs, data sources, and devices, simplifying the setup and configuration process.
- These templates can be customized and extended, making it easy to apply consistent settings across multiple devices.
User Interface:
- Cacti provides a web-based interface for managing and viewing network performance data.
- The interface is designed to be user-friendly, with options for creating and editing graphs, managing data sources, and configuring devices.
Scalability:
- Cacti is designed to handle large-scale environments, capable of monitoring hundreds or thousands of devices.
- It can be extended and customized to meet the needs of large enterprises as well as smaller networks.
Alerts and Notifications:
- Cacti can be configured to send alerts and notifications based on predefined thresholds and conditions.
- This helps administrators respond promptly to network issues and performance problems.
Plugins:
- The functionality of Cacti can be extended through a variety of plugins, which add additional features and capabilities.
- Plugins are available for enhanced graphing, additional data collection methods, user authentication, and more.

Use Cases for Cacti
- Network Performance Monitoring: Track bandwidth usage, latency, and other performance metrics for routers, switches, and other network devices.
- Server Monitoring: Monitor the performance and resource utilization of servers, including CPU usage, memory usage, disk activity, and more.
- Capacity Planning: Analyze historical data to predict future resource needs and plan for network and infrastructure upgrades.
- Troubleshooting: Identify and diagnose network and server performance issues by visualizing trends and anomalies in collected data.
- Reporting: Generate reports and dashboards to provide insights into network performance for management and stakeholders.
Read Also: Install Cacti on Rocky Linux 9
Conclusion
Cacti is a powerful and flexible tool for network monitoring and graphing, suitable for a wide range of environments from small networks to large enterprises. Its ability to collect and visualize data, combined with its scalability and extensibility, makes it a valuable asset for IT professionals and network administrators.
Linux Server Specification
We are using a minimal CentOS 8 KVM machine with following specification.
- CPU – 3.4 Ghz (2 cores)
- Memory – 2 GB
- Storage – 20 GB
- Operating System – CentOS 8.2
- Hostname – cacti-01.centlinux.com
- IP Address – 192.168.116.206 /24
For setting up a Cacti server on CentOS 8, you’ll need a machine with at least 2 GB RAM, 20 GB of storage, and a stable internet connection. If you don’t have a spare physical server or want a convenient, low-cost option for experimenting with Linux servers, consider using a Mini PC or a VPS from Rose Hosting.
Mini PCs offer a compact, energy-efficient way to run your own server at home, while Rose Hosting VPS provides a hassle-free cloud-based environment perfect for testing and production workloads.
Both options are excellent for learning and deploying Linux server applications like Cacti without investing in bulky hardware. (Affiliate links included below for Mini PCs and Rose Hosting VPS for your convenience.)
[Power Your Projects with the Best Mini PC – Shop Now!]
[Discover the Power of Rose Hosting VPS – Limited Time Offer!]
Disclaimer: This post contains affiliate links, which means we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you if you decide to purchase through these links. This helps us maintain and improve our content.
Upgrade Linux Software Packages
Connect with cacti-01.centlinux.com as root user by using a ssh tool.
First of all, we are upgrading the existing software packages of our CentOS 8 server.
dnf update -yOur CentOS 8.1 machine has been upgraded to CentOS 8.2. We can confirm it by using following commands.
uname -a
cat /etc/redhat-releaseOutput:
Linux cacti-01.centlinux.com 4.18.0-193.6.3.el8_2.x86_64 #1 SMP Wed Jun 10 11:09:32 UTC 2020 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
CentOS Linux release 8.2.2004 (Core)
You can follow our previous post to upgrade CentOS 7 to 8 Server.
Installing Apache Web Server
Cacti network monitoring server is a PHP based web application, therefore, we need a PHP supported web browser to run it.
We are using the popular Apache HTTP Server for this purpose.
dnf install -y httpd httpd-develEnable and start Apache service.
systemctl enable --now httpd.serviceAllow the Apache Service in Linux firewall, to make it accessible from the network computers.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
firewall-cmd --reloadInstalling MariaDB Database Server
Cacti requires a MySQL database for its metadata repository. Therefore, we are installing MariaDB server. Please follow our previous article, if you want to install latest version of MariaDB on CentOS 8.
dnf install -y mariadb-serverEnable and start MariaDB database service.
systemctl enable --now mariadb.serviceConfigure MariaDB Server and set the password of root user.
mysql_secure_installationOutput:
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] Y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
Install PHP on CentOS 8
Cacti is developed in PHP programming language, thus it requires a PHP supported web server to run. We have already installed Apache HTTP Server and now we are installing PHP on CentOS 8.
dnf install -y php-fpm php-common php-mysqlnd php-xml php-ldap php-json php-cli php-gd php-gmp php-mbstring php-processEnable and start PHP-FPM Service.
systemctl enable --now php-fpm.serviceInstall SNMP on CentOS 8
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is an Internet standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks.
Install net-snmp and net-snmp-utils packages to install SNMP and php-snmp to enable PHP support for SNMP.
dnf install -y net-snmp php-snmp net-snmp-utilsInstall RRDTool on CentOS 8
Cacti requires RRDTool (RRD stands for Round Robin Database) for maintaining system metrics data. Therefore, we are installing rrdtool package using dnf command.
dnf install -y rrdtoolConfigure PHP Settings for Cacti Server
To use Cacti network monitoring server, we need to customize PHP settings accordingly.
Edit /etc/php.ini configuration file and configure it for using Cacti.
vi /etc/php.iniLocate and set following parameters therein.
safe_mode = Off ; Disable safe mode
date.timezone = "Asia/Karachi" ; Define timezone to avoid warnings on time/date functions
file_uploads = On ; Allow import of templates
memory_limit = 400M ; maximum amount of memory a PHP script can consume
max_execution_time = 60 ; maximum execution time (in seconds) of a PHP scriptInstall Cacti Server on CentOS 8
We are downloading latest stable version of Cacti from their official website.
cd /tmp
wget https://www.cacti.net/downloads/cacti-1.2.12.tar.gzExtract downloaded tarball into default DOCUMENT_ROOT.
tar -C /var/www/html -xzf cacti-1.2.12.tar.gz
cdRename the Cacti directory to a simple name for easy accessibility.
mv /var/www/html/cacti-1.2.12 /var/www/html/cactiCreate a MariaDB Database for Cacti Server
Connect with MariaDB server as root user.
mysql -u root -p123Create a database for Cacti network monitoring server.
create database cacti CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;Create a user for Cacti software and grant complete rights on cacti database.
GRANT ALL ON cacti.* TO cacti@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'Str0ngPa55word';Grant Time Zone selection privilege to cacti user.
GRANT SELECT ON mysql.time_zone_name TO cacti@localhost;Reload privileges tables.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Exit from MySQL shell.
QUITCacti tarball also contains a SQL script for creating the necessary database objects. We can use this script to create tables and other objects in the cacti database.
mysql -D cacti -u cacti -pStr0ngPa55word < /var/www/html/cacti/cacti.sqlBefore moving forward, we need to load the MariaDB timezone tables. Otherwise, the Cacti web installer will give you warning on timezones.
Use following command to load timezone tables with available timezones from CentOS 8 operating system.
mysql_tzinfo_to_sql /usr/share/zoneinfo | mysql -u root -p123 mysqlOutput:
Warning: Unable to load '/usr/share/zoneinfo/leapseconds' as time zone. Skipping it.
Warning: Unable to load '/usr/share/zoneinfo/tzdata.zi' as time zone. Skipping it.
Timezones has been successfully loaded into MariaDB tables. Don’t worry about the warnings, it is because these files do not contain a valid timezone.
Edit MariaDB configuration file.
vi /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnfSet following global variables under [mysqld] section, as required by Cacti network monitoring software.
join_buffer_size=30M
innodb_file_format=Barracuda
innodb_buffer_pool_size=256M
innodb_buffer_pool_instances=1
innodb_flush_log_at_timeout=3
innodb_read_io_threads=32
innodb_write_io_threads=16
innodb_io_capacity=5000
innodb_io_capacity_max=10000
innodb_large_prefix=1
character_set_client=utf8mb4
character_set_server=utf8mb4
collation_server=utf8mb4_unicode_ciConfigure Cacti Server on CentOS 8
Edit config.php file and update parameters according to your environment.
vi /var/www/html/cacti/include/config.phpLocate and update following parameters.
$database_username = 'cacti';
$database_password = 'Str0ngPa55word';Make apache user as owner of the Cacti software directory.
chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/cacti/Restart Apache and PHP services to apply changes.
systemctl restart httpd.service php-fpm.serviceConfigure SELinux for Cacti Server
Install required SELinux commands i.e. semanage by using dnf command..
dnf install -y policycoreutils-python-utils-2.9-9.el8.noarchConfigure SELinux to allow read/write on the following directories.
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/cacti/log(/.*)?"
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/cacti/resource/snmp_queries(/.*)?"
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/cacti/resource/script_server(/.*)?"
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/cacti/resource/script_queries(/.*)?"
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/cacti/scripts(/.*)?"
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/cacti/cache/boost(/.*)?"
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/cacti/cache/mibcache(/.*)?"
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/cacti/cache/realtime(/.*)?"
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/cacti/cache/spikekill(/.*)?"
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/var/www/html/cacti/rra(/.*)?"Reapply the filecontexts on the cacti directory.
restorecon -R /var/www/html/cacti/Configure a cron job to run poller.php script in every 5 minutes. This script will collect and update the system metrics in /rra directory.
echo "*/5 * * * * apache /usr/bin/php /var/www/html/cacti/poller.php > /dev/null 2>&1" >> /etc/crontabOpen URL http://cacti-01.centlinux.com/cacti in a client’s browser such as Google Chrome.
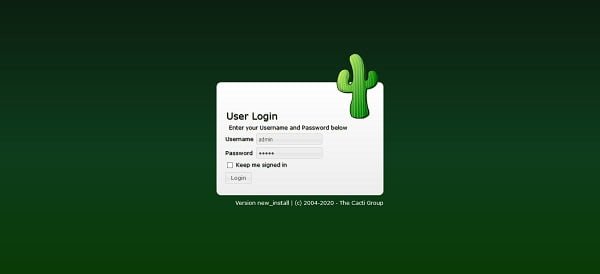
Login by using default username/password i.e. admin/admin
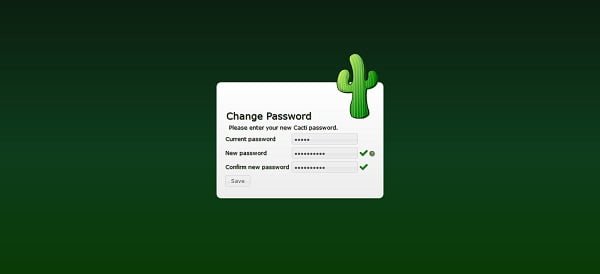
Since, we are login to Cacti web interface for the first time, therefore, we are required to change the default password of admin user.
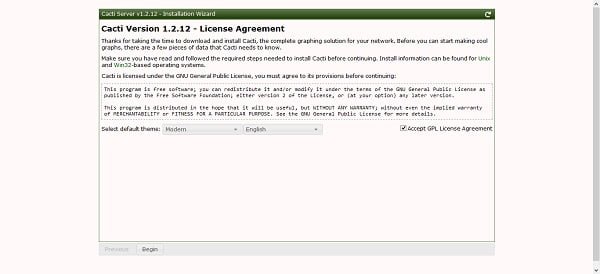
Read and accept the License Agreement of Cacti network monitoring software.
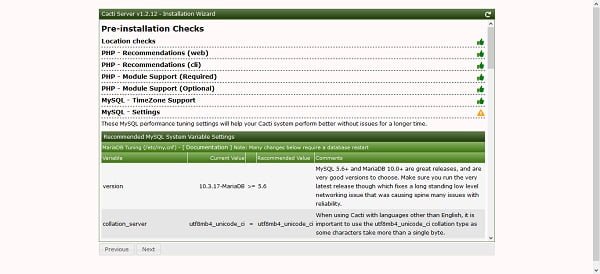
If you have followed the installation steps in this article correctly, then you won’t found any warning on this page.
We are skipping a warning about innodb_buffer_pool_instances, a MariaDB global variable, because we are installing MariaDB on a machine with limited memory. If you install MariaDB on a machine with more than 1 GB RAM available for InnoDB buffer, you won’t see this warning.
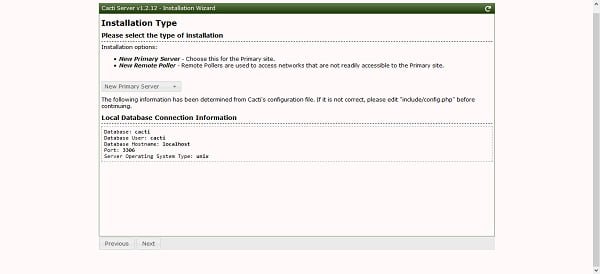
Choose your preferred installation type. Since, this is our first Cacti server therefore, we have selected “New Primary Server”.
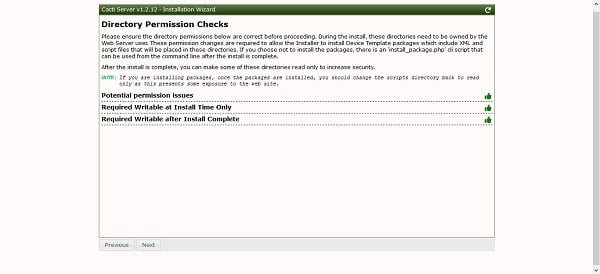
If you have configured the SELinux correctly, then there won’t be any warnings.
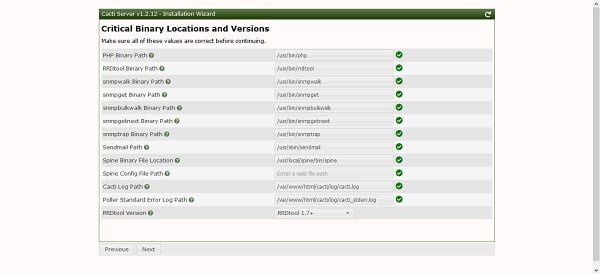
Setup is checking for required binaries, their locations and required versions.
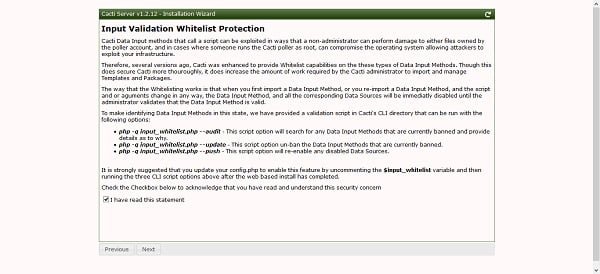
Setup will inform you about a security concern and how to handle it. Accept it and continue.
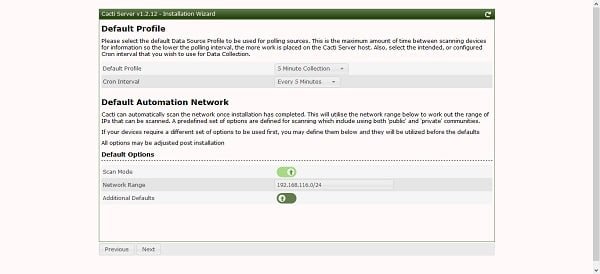
Adjust your default profile and continue.
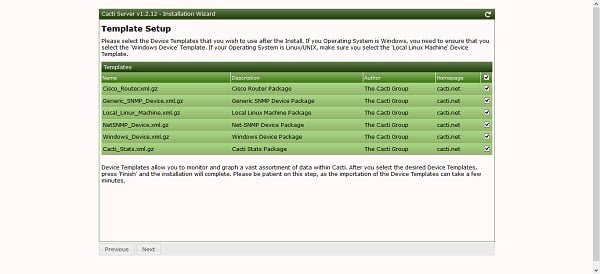
Select the required device templates and continue.
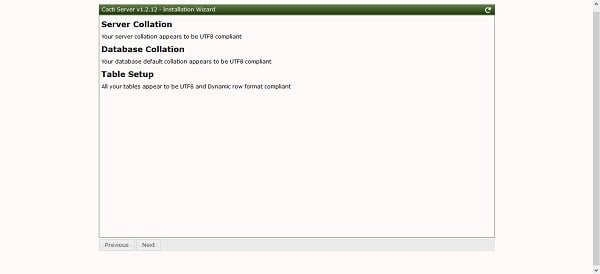
Setup is checking the MariaDB server and database collation.
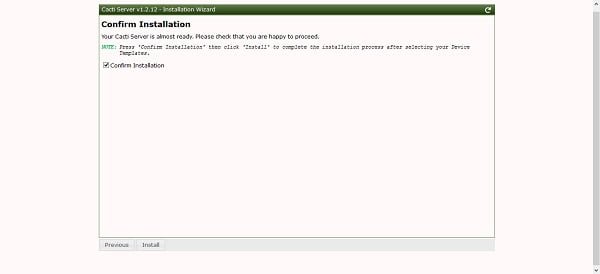
If your configurations are fine, then Cacti setup will display this page and it will ask you to start installation.
We have successfully install Cacti on CentOS 8.
After successful installation, you will reached at the Cacti Dashboard.
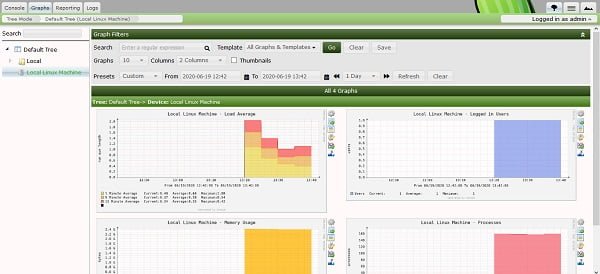
You can see some graphs by clicking on the Graphs tab.
Final Thoughts
Cacti is an invaluable tool for network and server performance monitoring, providing detailed insights and visualizations to help manage and optimize your infrastructure. Installing and configuring Cacti on CentOS 8 can significantly enhance your ability to track and analyze network metrics, ensuring your systems run smoothly and efficiently.
If you need expert guidance on setting up Cacti Server on Linux Server, I offer a comprehensive service to help you through the process. From installation to configuration and optimization, I’ll ensure your Cacti setup is tailored to your specific needs and runs seamlessly.
Need a dependable Linux system administrator? I specialize in managing, optimizing, and securing Linux servers to keep your operations running flawlessly. Check out my services!
FAQs
1. Can I install Cacti on CentOS 8 without a GUI (graphical interface)?
Yes, Cacti works perfectly on a server without a GUI, as it is accessed via a web browser remotely.
2. What is the minimum PHP version required for Cacti on CentOS 8?
Cacti requires PHP 7.2 or higher on CentOS 8 for full compatibility.
3. How do I secure Cacti after installation?
Use strong passwords, configure a firewall to restrict access, and keep your system and Cacti updated regularly.
4. Is it necessary to install a database before setting up Cacti?
Yes, Cacti needs MySQL or MariaDB installed and configured before installation to store its data.
5. Can I monitor multiple servers with a single Cacti installation?
Absolutely, Cacti can monitor multiple devices and servers from one installation using SNMP.
Recommended Courses
If you’re serious about mastering IT infrastructure monitoring, the Zabbix Application and Network Monitoring by Sean Bradley course is a must-have resource. This practical training walks you through real-world scenarios to monitor servers, applications, and networks with confidence, making it ideal for system administrators, DevOps engineers, and IT professionals aiming to level up their skills. By enrolling, you’ll gain hands-on knowledge that can save countless hours in troubleshooting and system management. [Click here to check out the course]
Disclaimer: This link is an affiliate link, which means I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you if you decide to purchase through it. This helps support my blog and allows me to continue creating useful content.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.