Learn how to install LAMP stack on Docker with this step-by-step guide. Set up Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP in isolated containers for efficient and scalable web development. Perfect for beginners and advanced users. #centlinux #linux #docker
Table of Contents
What is LAMP Stack?
The LAMP stack is a popular set of open-source software used together to create dynamic websites and web applications. LAMP stands for:
- Linux: The operating system that forms the foundation of the stack. It’s known for its stability, security, and flexibility.
- Apache: The web server software that handles HTTP requests and serves web content to users. It’s highly customizable and widely used.
- MySQL: The relational database management system that stores and manages the data for your web application. It’s known for its reliability and performance.
- PHP: The server-side scripting language used to develop dynamic web pages. PHP processes the business logic and interacts with the database to generate web content.
Key Features
- Open Source: All components of the LAMP stack are free and open-source, making it a cost-effective solution.
- Widely Supported: There is extensive community support and a vast amount of documentation available.
- Flexibility: Each component can be replaced or upgraded independently, providing flexibility in configuration.
- Performance: Optimized for performance, making it suitable for high-traffic websites and applications.
- Security: Proven track record of security, with regular updates and a strong focus on secure coding practices.
Use Cases
- Web Development: Ideal for developing dynamic websites and web applications.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Commonly used as the foundation for popular CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
- E-commerce Platforms: Frequently used in building and running e-commerce websites due to its robustness and scalability.
- Prototyping and Testing: Useful for developers to quickly prototype and test web applications.
The LAMP stack’s combination of Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP offers a powerful and versatile environment for web development, making it a popular choice among developers worldwide.
We are already learned how to install LAMP stack on Ubuntu. But this is now the era of DevOps and it is necessary to explore how to install LAMP Stack on Docker.

LAMP Stack Alternatives
There are several alternatives to the traditional LAMP stack, each offering different combinations of technologies to suit various needs and preferences in web development. Here are some popular alternatives:
1. LEMP Stack
- Linux: Operating system.
- Nginx: Web server, known for its performance and ability to handle many concurrent connections.
- MySQL/MariaDB: Relational database management system.
- PHP/Python/Perl: Server-side scripting languages.
2. MEAN Stack
- MongoDB: NoSQL database for storing JSON-like documents.
- Express.js: Web application framework for Node.js.
- Angular: Front-end web application framework.
- Node.js: JavaScript runtime for server-side programming.
3. MERN Stack
- MongoDB: NoSQL database.
- Express.js: Web application framework.
- React: Front-end library for building user interfaces.
- Node.js: JavaScript runtime.
4. LEPP Stack
- Linux: Operating system.
- Nginx: Web server.
- PostgreSQL: Object-relational database management system.
- PHP/Python/Perl: Server-side scripting languages.
5. JAM Stack
- JavaScript: For dynamic functionalities.
- APIs: Backend services are abstracted into reusable APIs.
- Markup: Static site generators for serving pre-rendered HTML files.
6. WAMP Stack
- Windows: Operating system.
- Apache: Web server.
- MySQL/MariaDB: Relational database management system.
- PHP: Server-side scripting language.
7. XAMPP
- Cross-platform: Supports multiple operating systems (Windows, Linux, macOS).
- Apache: Web server.
- MySQL: Relational database management system.
- PHP/Perl: Server-side scripting languages.
8. Serverless Architecture
- AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions: Run code in response to events without provisioning or managing servers.
- API Gateway: Manage APIs and serve as a “front door” for applications.
- DynamoDB, Firestore: NoSQL databases provided by cloud providers.
9. Docker and Kubernetes
- Containers: Use Docker to containerize applications for consistent environments.
- Orchestration: Use Kubernetes for managing containerized applications at scale.
10. DigitalOcean App Platform
- Managed PaaS: Deploy, manage, and scale applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
- Supports multiple languages and frameworks: Node.js, Python, Ruby, PHP, Go, etc.
Each of these alternatives offers different advantages, depending on the specific requirements of the project, such as the need for performance, scalability, ease of development, or the preference for certain programming languages or databases.
Recommended Training: Docker for the Absolute Beginner – Hands On – DevOps from Mumshad Mannambeth

Docker Host Specification
We are using a Linux based Docker host with following specification.
- CPU – 3.4 Ghz (2 cores)
- Memory – 2 GB
- Storage – 20 GB
- Operating System – Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS
- Hostname – docker-01.centlinux.com
- IP Address – 192.168.116.218 /24
Read Also: How to install LAMP on Rocky Linux 9
Although there are many pre-build single LAMP images are available on Docker Hub. But by following the best practice and to maintain the modularity of the software stack, we will run each service in its relevant container.
havit HV-F2056 15.6″-17″ Laptop Cooler Cooling Pad – Slim Portable USB Powered (3 Fans), Black/Blue
$23.79 (as of July 9, 2025 21:12 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Configure a PHP/Apache Docker Container
Connect with Docker host (docker-01.centlinux.com) as a privileged user by using a ssh tool.
Create a directory to store files related to our LAMP Server.
mkdir ~/lamp-server
cd ~/lamp-server/Create a directory that will be mounted as Apache Document Root within the Apache container. This directory is used to deploy our web applications and the php-apache Docker container will serve our web applications to clients.
mkdir ~/lamp-server/htmlCreate a default PHP page in this directory. The PHP script contains a single phpinfo() function, that generates a webpage with detailed information about Apache server and installed plugins.
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" > ~/lamp-server/html/index.phpWe need to install some additional PHP plugins on the php-apache Docker container. For this purpose, we have to create the build context file for our php-apache Docker container.
Create a directory to store php-apache build context.
mkdir php-apacheCreate build context file for php-apache Docker container.
vi php-apache/DockerfileAdd following directives there in.
FROM php:7.4-apache
RUN docker-php-ext-install pdo pdo_mysql mysqliSince, we are deploying a multi-container Docker application, therefore, we need to use docker-compose to create and execute our containers.
For this purpose, we need to create docker-compose.yml file that contains the directives to create our containers.
vi docker-compose.ymlAnd add following directives to create php-apache container.
version: '3'
services:
php-apache:
build:
context: ./php-apache
ports:
- 80:80
volumes:
- ./html:/var/www/html
links:
- 'mariadb'Configure MariaDB Docker Container
Create a directory for Dockerfile that will be used to create mariadb Docker container.
mkdir -p mariadb/sqlCreate a SQL script to prepare our sample table.
vi mariadb/sql/init-db.sqlAdd following SQL statements in this file.
USE testdb;
CREATE TABLE test (
name varchar(30),
email varchar(50)
);
INSERT INTO test (name, email)
VALUES
('Ahmer', 'ahmer@centlinux.com'),
('Mansoor','mansoor@centlinux.com'),
('Salman','salman@centlinux.com');Create a Dockerfile to customize our mariadb Docker container.
vi mariadb/DockerfileAdd the following build context there in.
FROM mariadb:10.5
ENV MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD 123
ENV MYSQL_USER ahmer
ENV MYSQL_PASSWORD 123
ENV MYSQL_DATABASE testdb
COPY ./sql /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/Create a directory on Docker Host to store MariaDB Server data files. This directory will be mounted within the MariaDB Docker container on startup.
mkdir mariadb_dataNow, configure a MariaDB docker container in the same docker-compose.yml file.
vi docker-compose.ymlAppend following lines of code under the “services” section in this file.
mariadb:
build:
context: ./mariadb
volumes:
- ./mariadb_data:/var/lib/mysql8Bitdo Retro Mechanical Keyboard, Bluetooth/2.4G/USB-C Hot Swappable Gaming Keyboard with 87 Keys, Dual Super Programmable Buttons for Windows and Android – N Edition
$89.98 (as of July 9, 2025 21:12 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Install LAMP Stack in Docker
Start our LAMP stack environment by using docker-compose command.
sudo docker-compose upOutput:
...
Starting lamp-server_mariadb_1 ... done
Starting lamp-server_php-apache_1 ... done
Attaching to lamp-server_mariadb_1, lamp-server_php-apache_1
...
mariadb_1 | 2020-02-28 17:46:24 0 [Note] InnoDB: Buffer pool(s) load completed at 200228 17:46:24
Open URL http://docker-01.centlinux.com in a web browser.
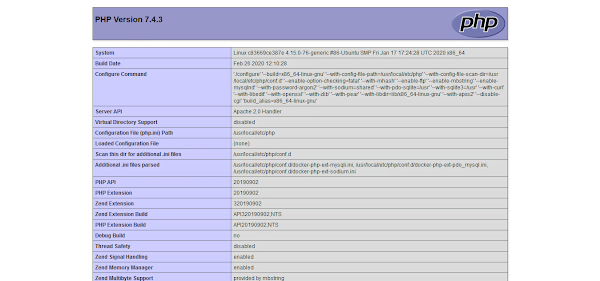
Our LAMP Stack has been serving the default PHP page that we have created above.
Connect PHP Application with MariaDB Database
To demonstrate the connectivity between php-apache and mariadb Docker containers, we are creating a PHP webpage that creates connection to MariaDB database to fetch and display the data from a database table.
For this purpose, we are replacing the existing index.php with a new webpage that contains the PHP code to accomplish the required task..
mv html/index.php html/phpinfo.php
vi html/index.phpAdd following HTML code in this file.
<html>
<head>
<title>Fetching Data from MariaDB Server</title>
</head>
<body>
<style>
td,th {
border: solid black 1px;
font-size: 30px;
width: 200px;
}
</style>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
</tr>
<?php
$dbhost = "mariadb";
$dbuser = "ahmer";
$dbpass = "123";
$db = "testdb";
$dbconn = mysqli_connect($dbhost, $dbuser, $dbpass, $db);
if(! $dbconn ) {
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
$query = mysqli_query($dbconn, "SELECT * FROM test")
or die (mysqli_error($dbconn));
while ($row = mysqli_fetch_array($query)) {
echo
"<tr>
<td>{$row['name']}</td>
<td>{$row['email']}</td>
</tr>";
}
mysqli_close($dbconn);
?>
</body>
</html>Open URL http://docker-01.centlinux.com in a web browser.

You can see that, our web page is now displaying data from the test table.
Linux Pocket Guide: Essential Commands (Linux Pocket Guides)
$19.75 (as of July 10, 2025 21:22 GMT +00:00 – More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)Final Thoughts
Setting up the LAMP stack on Docker provides a flexible and efficient environment for web development, allowing you to run your applications in isolated containers for better performance and scalability. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, Docker can simplify the deployment and management of your LAMP stack.
If you need assistance with installing the LAMP stack on Docker, I offer a comprehensive service on Fiverr. This service includes:
- Step-by-step installation of the LAMP stack on Docker
- Configuration and optimization for performance
- Setup of containers for Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP
- Guidance on best practices for container management
Whether you need cloud optimization, server management, or automation, I provide comprehensive AWS and Linux services. Hire me on Fiverr to elevate your systems.
Let me help you get started with Docker and the LAMP stack today!




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.